This document explains the different methods that you can use to request capacity in Capacity Planner. To learn more about the features and use cases for Capacity Planner, see instead Capacity Planner overview.
To help ensure that your Google Cloud project, folder, or organization has sufficient capacity for expected or unexpected growth, you can request capacity for a future date and time. Based on your requirements for cost, assurance level, and resource type, you can use either capacity requests (for best-effort assurance) or future reservation requests (for high-level assurance).
Comparison of methods to request capacity
The following table summarizes the key differences between the methods that you can use to request capacity in Capacity Planner. To help you choose the method that best fits your workload's needs, you can also use the flowchart in this document.
| Capacity requests | Future reservation requests | |
|---|---|---|
| Summary | Use capacity requests to indicate your needs for capacity.
Capacity requests help reduce the risk of resource availability errors
during unexpected growth in usage. With capacity requests, you inform
Google Cloud that you need a large number of resources, but
without committing to pay for resources that you might not use.
|
Use future reservation requests to obtain a high-level assurance for capacity. Future reservation requests give you high-level assurance that resources available when you need them, and give you exclusive access to those resources during your reservation period. |
| Use cases |
Ideal for indicating potential needs of a large number of resources, such as in the following cases:
|
Ideal for obtaining capacity with a high-level assurance, such as in the following cases:
|
| Supported locations | Multiple regions or zones. In a single capacity request, you can request resources across multiple regions or zones. | Single zone. In a single future reservation request, you can only request resources in a single zone. |
| Supported resources | By using capacity requests, you can request resources such as the following:
For a full list of supported resources, contact your assigned technical account manager (TAM). |
By using future reservation requests, you can request the following
Compute Engine resources:
|
| Capacity assurance | Best-effort assurance. Google Cloud makes best-effort attempts to deliver your requested capacity. Even if Google Cloud approves a capacity request, your requested resources are still subject to real-time availability. Thus, Google Cloud might only deliver and hold part, or none, of your requested resources during your requested period. | Very-high assurance. You have a very high assurance that Compute Engine delivers your request capacity at the start of your chosen reservation period. You have exclusive access to your reserved resources for that period, preventing others from using them. |
| Capacity delivery | At your specified date and time, Google Cloud helps ensure that you can use your requested resources without encountering resource availability errors. | 24 hours before the start of your reservation period, Compute Engine provisions your reserved resources by automatically creating on-demand reservations. After the start of the reservation period, you can start using the on-demand reservations by creating instances. For more information, see Consume an automatically consumed reservation. |
| Pricing |
For capacity requests, you incur charges as follows:
|
For future reservation requests, you incur charges as follows:
|
| Quota | If you have insufficient quota for your requested capacity, then Google Cloud increases quota on your behalf before capacity is delivered. | You must have sufficient quota for the resources that you're reserving when you create a request and, if the request is approved, at the start of the reservation period. Otherwise, Compute Engine delivers only part of your reserved capacity. |
| Review timeline | The time that Google Cloud takes to review a capacity request varies based on the type and number of resources that are specified in the request. | Google Cloud typically reviews a future reservation request within five days. If Google Cloud needs more time or has questions about your request, then your TAM contacts you. |
| Creation method | To create a capacity request and use the requested requested
resources, follow these steps:
|
To create a future reservation request and use the reserved resources,
follow these steps:
|
Choose a method to request capacity
Use the following flowchart to choose the method to request capacity that best fits your workload needs:
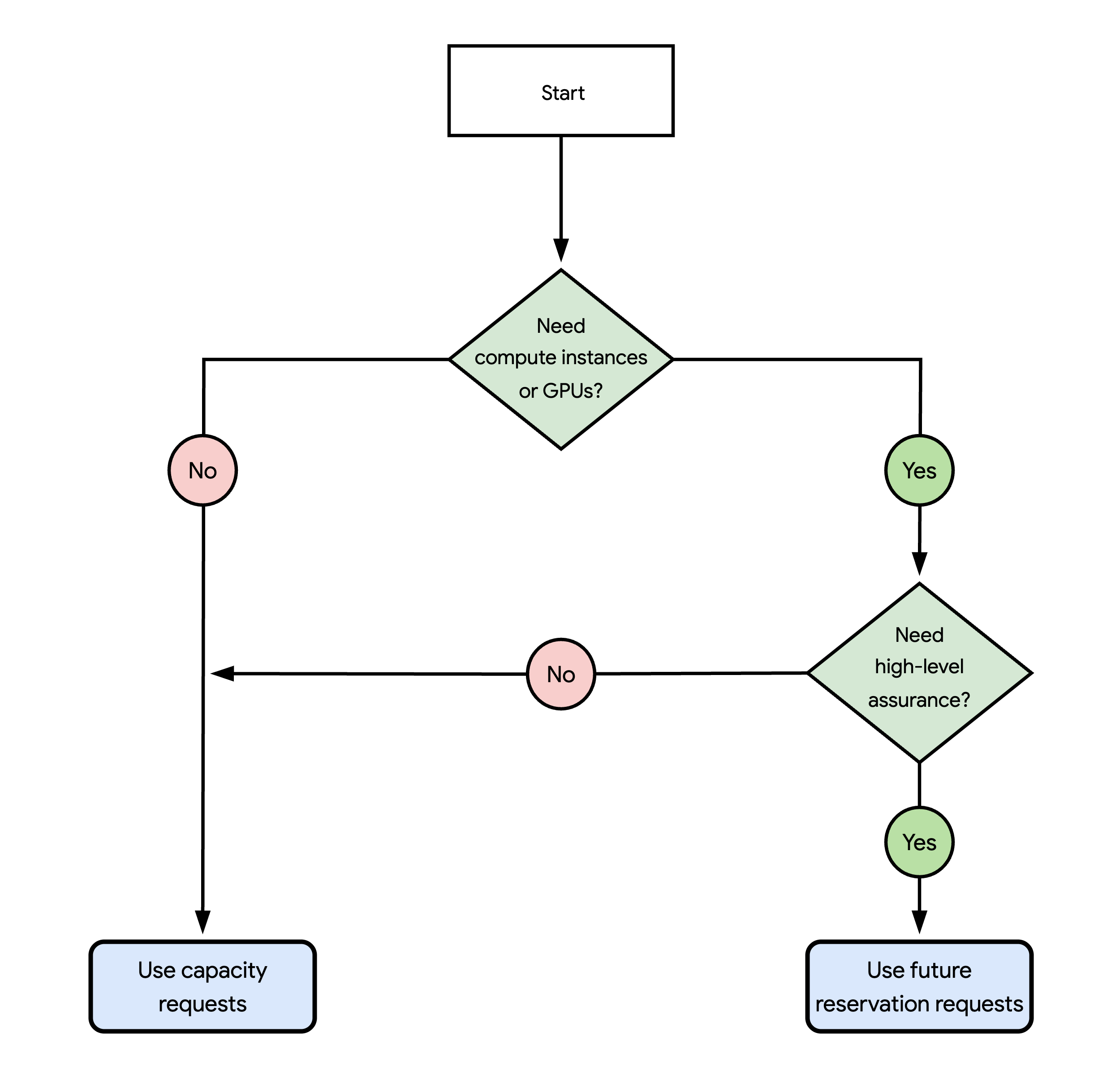
The questions in the preceding diagram are the following:
Do you need resources for creating compute instances or GPUs?
Yes: Go to the next question.
Do you need a high-level of assurance for your requested resources?
Use capacity requests
Use capacity requests to inform Google Cloud that you need a large number of resources across multiple regions or zones. After you create a capacity request, the time that Google Cloud takes to review it varies based on the type and number of resources that are specified in your request. If approved, then Google Cloud schedules the provisioning of your requested resources on your chosen date and time. However, because the resources obtained through capacity requests are subject to real-time availability, Google Cloud might provision only part, or none, of your requested resources. You pay only for the provisioned resources that you use.
For more information about the requirements and limitations that you apply when you create capacity requests, see About capacity requests.
Use future reservation requests
Use future reservation requests to reserve resources in a single zone. After you create a request, Google Cloud typically reviews your request within five days. If approved, then Compute Engine creates on-demand reservations with your requested capacity on your chosen date and time. You have exclusive access to your reserved resources during your reservation period, preventing others from using them. You also commit to pay for the reserved resources for the entire reservation period, whether you use the resources or not.
For more information about the requirements and limitations that you apply when you create future reservation requests, see About future reservation requests.
