This document explains the requirements and limitations that you apply when you create a capacity request.
You can use capacity requests to inform Google Cloud that you need a large number of resources for a future date and time, and across multiple regions or zones. This approach helps ensure that your Google Cloud project has sufficient capacity to prevent resource availability errors during unexpected growth, such as in the following scenarios:
Event-based planning
Migrations to Google Cloud
Product launches and expansions
Workloads with changing requirements
When you use capacity requests, you get best-effort assurance for the capacity that Google Cloud provisions, and you only pay for resources when you use them. These features differ from future reservation requests, which give you a higher assurance for capacity in a specific zone, but require you to pay for resources for your entire reservation period, regardless of usage.
If you aren't sure whether capacity requests or future reservation requests are better for your use case, then see instead Choose a method to request capacity.
Understand capacity requests
Capacity requests have the following benefits:
Best-effort assurance for large requests of capacity: when you create a capacity request and Google Cloud approves it, Google Cloud makes best-effort attempts to provision your requested resources and hold them for the duration of your requested period. Your requested resources are subject to real-time availability, and Google Cloud may provision or hold only part, or none, of your requested resources. This approach helps you to not commit to paying for capacity that you might not use.
Request resources across multiple regions or zones: you can request a large number of resources across multiple regions or zones in a single capacity request. This approach helps increase the resilience of your workload.
You pay as you go (PAYG): after Capacity Planner delivers your requested resources, you only incur charges when you use the requested resources. This approach helps you avoid paying for capacity that you don't use.
The following sections explain capacity requests properties, review process, and lifecycle.
Capacity request properties
To create a capacity request, you must contact your assigned technical account manager (TAM), and supply the following information about the resources that you want to request:
Project: the ID of the project where you want to create the capacity request.
Start time: the date and time when you want Google Cloud to deliver your requested resources, and you want to start using those resources.
End time: the date and time when you no longer need your requested resources. After this time, you can either keep using the requested resources, or agree with Google Cloud to gradually decrease your resource usage on a day-by-day basis.
Location: for each resource that you want to request, you must specify the region or zone where you want Google Cloud to provision those resources. You can request resources across multiple regions or zones.
Resources: the type and total number of resources that you want to have in your project at the start time. In a single capacity request, you can request one or more of the following resources simultaneously:
Compute Engine instances: the number of instances and machine types that you want to request. If you request a machine type that doesn't include Local SSD disks or GPUs by default, then you can also specify the type and number of Local SSD disks or GPUs to attach to your instances.
Disks: the number and type of disks that you want to request. For more information about the available disks in Compute Engine, see Choose a disk type in the Compute Engine documentation.
GPUs: instead of requesting entire instances with GPUs attached, you can only request specific GPU models and use them for creating Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters.
TPUs: the number of TPU chips and the TPU versions that you want to request.
Other resources: you can request other types of resources that Capacity Planner doesn't display usage and forecast for, such as the following:
BigQuery
Cloud Storage
Google Cloud networking products
Google Cloud VMware Engine
Vertex AI
For a full list of resources that you can request, contact your TAM.
After you supply the information about your capacity request properties, your TAM creates the capacity request on your behalf and submits it for review.
Capacity request review process
After your TAM creates a capacity request on your behalf and submits it for review, Google Cloud reviews your request. The time that Google Cloud takes to review your request varies based on the type and number of resources that are specified in the request.
When a capacity request is in review, one of the following can occur:
Google Cloud approves your request: Google Cloud makes best-efforts attempts to hold and deliver your requested capacity at your specified date and time. After Google Cloud approves a capacity request, you can't modify or withdraw it anymore.
Google Cloud puts the request on hold: Google Cloud has questions about your request because some of your requested resources aren't available. Your TAM contacts you to propose an update of your request. If you accept the update, then your TAM modifies the request and submits it again for review. Otherwise, Google Cloud declines your request. Contact your TAM to discuss your available options for requesting capacity in Google Cloud.
You withdraw the request: you cancel the capacity request before Google Cloud approves it, and Google Cloud declines the request.
Capacity request lifecycle
The following diagram shows the different states that Capacity Planner can set a capacity request to, from the request creation up to its deletion:
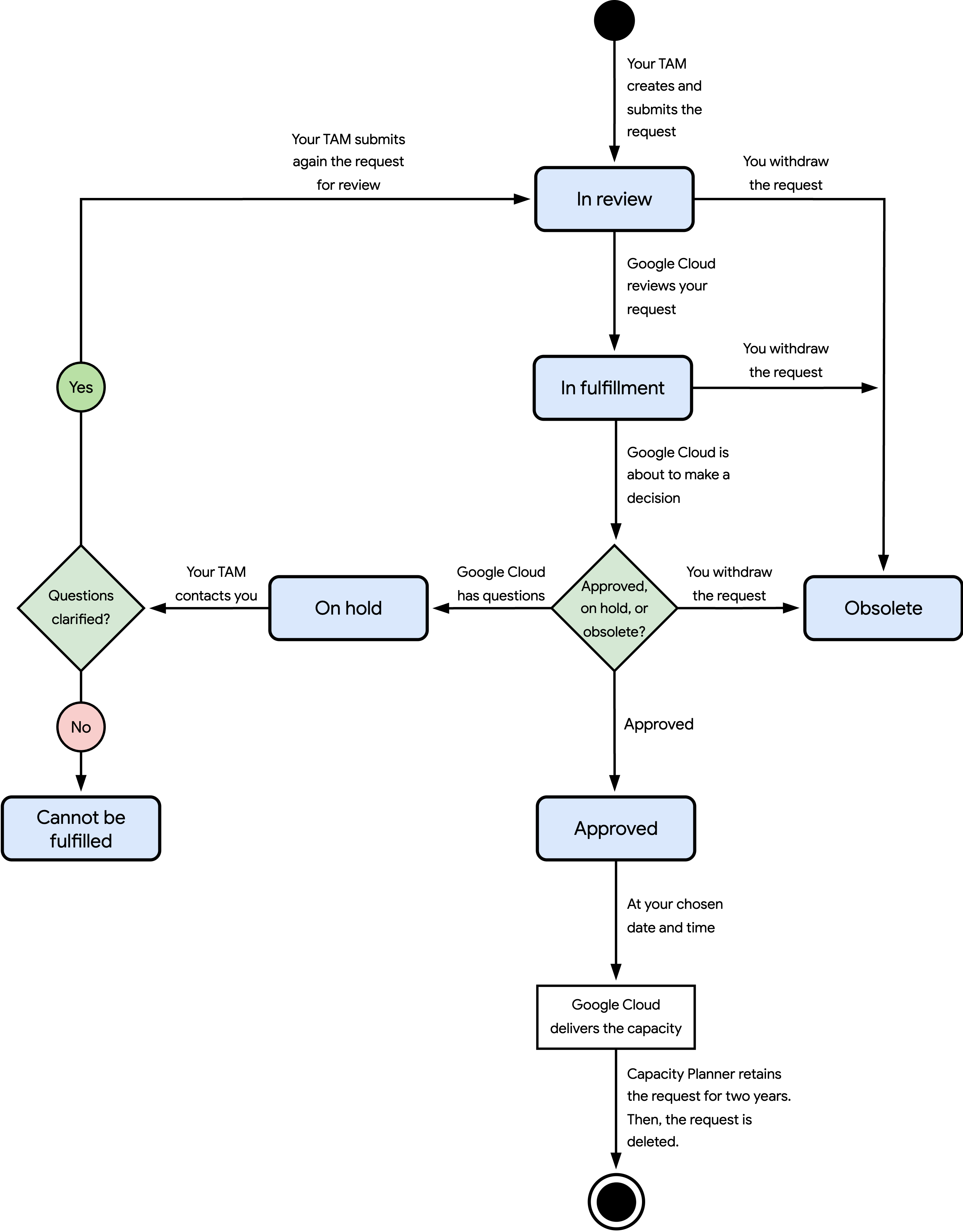
The states and flow of events shown in the preceding diagram are as follows:
In review: your TAM created the capacity request on your behalf, and the request is pending review from Google Cloud. When you view the details of a request, you can verify the review status of each resource that is specified in your request.
In fulfillment: Google Cloud is about to approve or put your request on hold. You can optionally withdraw your request if you don't need the requested resources anymore.
Approved: Google Cloud has approved your request, or a requested resource that is specified in your capacity request. Google Cloud plans to deliver your requested resources at your chosen date and time. However, your requested resources are subject to real-time availability. Google Cloud may only provision part, or none, of them. An approved capacity request exists for up to two years. After that time, Capacity Planner automatically deletes it.
On hold: Google Cloud has questions about your request. Some, or all, of your requested resources aren't available. Your TAM contacts you to propose an update to your request. If you accept the update, then your TAM modifies the request and submits it again for review. Otherwise, Google Cloud declines your request.
Cannot be fulfilled: Google Cloud declines your request because it can't deliver your requested resources. If you still want to request capacity, then contact your TAM to explore alternatives.
Obsolete: you withdraw the capacity request before Google Cloud approves it, and Google Cloud declines the request.
Provision requested resources
After Google Cloud approves a capacity request, Google Cloud schedules the provisioning of your requested resources at your specified date and time. After that time, you can start using those resources. Google Cloud makes best-effort attempts to help ensure that you don't encounter resource availability errors during your requested period.
Quota
If Google Cloud approves a capacity request, then, by your chosen date and time, Google Cloud increases your quota on your behalf, if needed, to help ensure that you have sufficient quota for your requested resources.
For more information about the quota that you need, review the quota documentation for each resource that you want to request, or contact your TAM.
Pricing
When you create a capacity request, you don't incur charges. Instead, you incur charges when you use the requested resources after Google Cloud provisions them.
Pricing varies based on the type and number of resources that you request. For more information, review the pricing documentation for each resource that you want to request, or contact your TAM.
Limitations
Capacity requests have the following limitations:
After Google Cloud approves a capacity request, you can't modify or withdraw it.
You can't create capacity requests with matching resources. Instead, if Google Cloud hasn't approved a capacity request yet, contact your TAM to modify your existing request.
