This guide walks you through a sample installation of Google Distributed Cloud (software only) on bare metal on OpenStack virtual machines (VMs) with supported operating systems. The deployment uses a script to simplify installation of a hybrid cluster in OpenStack VMs. The guide also shows you one way to enable load balancing as a Service (LBaaS). You can use the OpenStack LBaaS and the Kubernetes OpenStack Cloud Provider with Google Distributed Cloud to expose the Kubernetes services outside of the OpenStack cluster.
Google Distributed Cloud doesn't provision the OpenStack VMs automatically, and provisioning the VMs is outside the scope of this guide. To learn the VM requirements and review an example deployment, see the Terraform example to create OpenStack VMs.
The guide consists of the following sections:
Deploy Google Distributed Cloud
Configure the OpenStack Cloud Provider for Kubernetes in the installed cluster to integrate with the Octavia load balancers
Validate the OpenStack Cloud Provider for Kubernetes integration
This guide uses OpenStack Ussuri, but Google Distributed Cloud doesn't have a requirement for specific versions of OpenStack. The guide uses OpenStack VMs to provide you with a two-node proof of concept environment running on OpenStack. For production installation requirements for Google Distributed Cloud, see the installation prerequisites.
Example deployment
This guide provides you with an example deployment of a bare metal cluster on OpenStack that integrates with OpenStack LBaaS. You must understand and adjust the commands and configuration values to suit your OpenStack environment. The following diagram shows the resulting deployment:
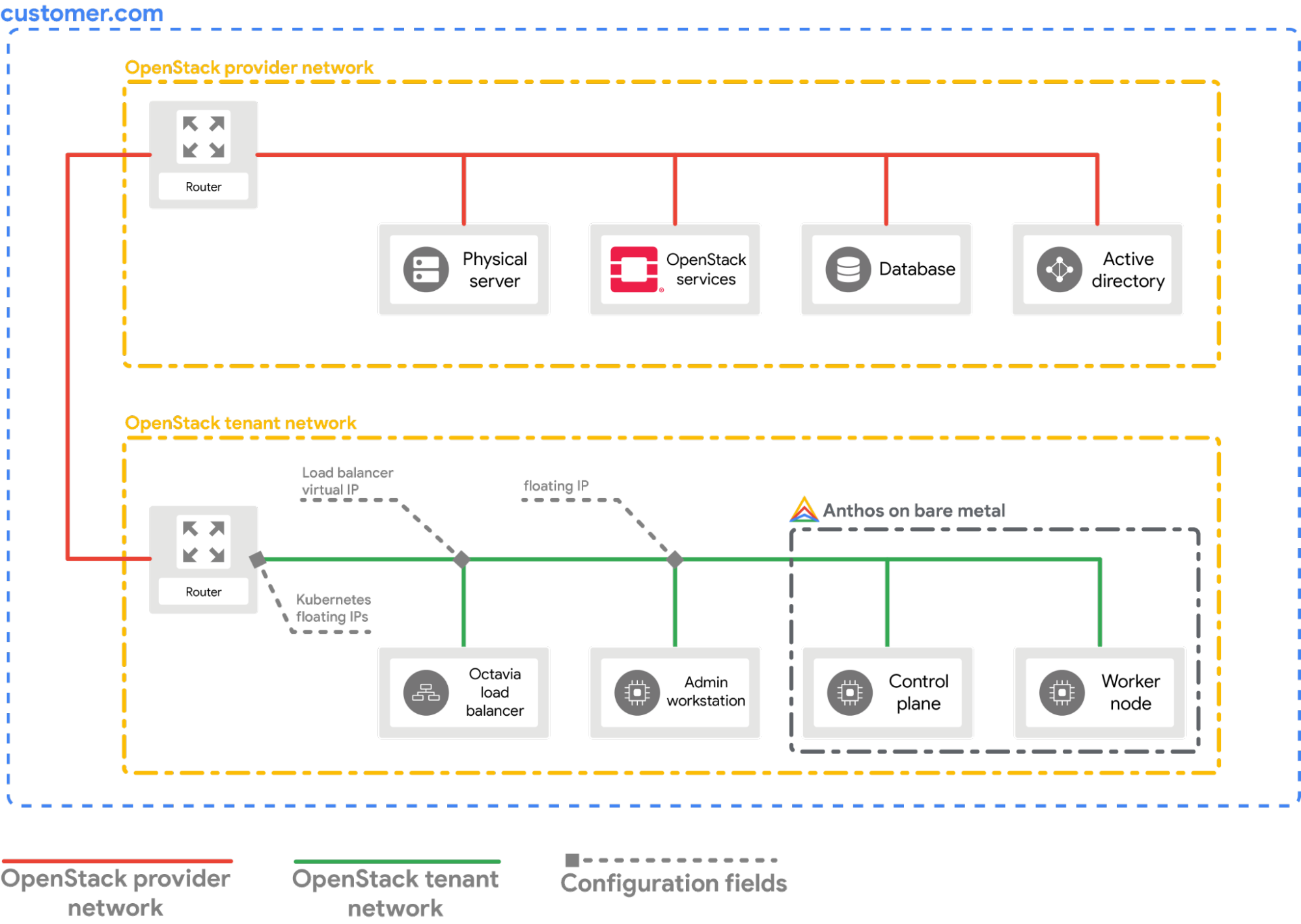
Prerequisites
- OpenStack Ussuri with LBaaS v2 deployed and functional
- Service account for downloading the bmctl tool
- Configure your OpenStack VMs and network as shown in the example deployment.
To provision a similar setup in your OpenStack environment, you have the
following options:
- Use this Terraform script to provision the resources automatically.
- Provision the resources manually.
- The following OpenStack VMs must be ready and available through SSH:
| Name | IP address | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| abm-ws |
10.200.0.10 (private IP) floating_ip (public IP) |
Acts as the admin workstation: It's used to deploy Google Distributed Cloud to the other machines. |
| abm-cp1 | 10.200.0.11 | Cluster control plane: This host runs the Kubernetes control plane and load balancer. |
| abm-w1 | 10.200.0.12 | Cluster worker node: This host runs the Kubernetes workloads. |
Deploy Google Distributed Cloud
This section shows you how to complete the following tasks:
- Install the tools you need on the
abm-wsadmin workstation VM. - Configure the project ID and service account needed to securely complete the deployment
- Create a cluster configuration file
- Create a cluster
Install the tools you need
Fetch the public floating IP address of the
abm-wsVM:export OPENSTACK_IPS=$(openstack floating ip list --tags=abm_ws_floatingip -f json) export FLOATING_IP=$(jq -c '.[]."Floating IP Address"' <<< $OPENSTACK_IPS | tr -d '"')Ensure you can use SSH to connect securely into the
abm-wsVM and sign in as arootuser. Therootuser configured by the Terraform scripts isabm.ssh ubuntu@$FLOATING_IP sudo -u abm -iVerify that you can use SSH to connect to the other nodes:
ssh abm@10.200.0.11 'echo SSH to $HOSTNAME succeeded' ssh abm@10.200.0.12 'echo SSH to $HOSTNAME succeeded'The expected responses for the preceding commands are:
SSH to abm-cp1 succeeded SSH to abm-w1 succeededDownload the
kubectlcommand line utility on theabm-wsVM.curl -LO "https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" chmod +x kubectl sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/sbin/Install Docker on the
abm-wsVM:curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh sh get-docker.sh sudo usermod -aG docker abm newgrp docker
Configure the Google Cloud project and service account
Obtain Google Cloud CLI access credentials for your user account.
These credentials are used with subsequent
gcloudcommands.gcloud auth loginMake sure the Google Cloud CLI is configured to use the Google Cloud project in which you want your cluster to be registered.
gcloud config set project PROJECT_IDSet the Application Default Credentials (ADC) for your user account in the admin workstation. This will be used when the
bmctltool is used for cluster creation.gcloud auth application-default loginCreate the
bm-gcrservice account. You use this service account to authenticate from the cluster.gcloud iam service-accounts create bm-gcr gcloud iam service-accounts keys create bm-gcr.json \ --iam-account=bm-gcr@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.comEnable the necessary APIs:
gcloud services enable \ anthos.googleapis.com \ anthosaudit.googleapis.com \ anthosgke.googleapis.com \ cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com \ connectgateway.googleapis.com \ container.googleapis.com \ gkeconnect.googleapis.com \ gkehub.googleapis.com \ gkeonprem.googleapis.com \ iam.googleapis.com \ logging.googleapis.com \ monitoring.googleapis.com \ opsconfigmonitoring.googleapis.com \ serviceusage.googleapis.com \ stackdriver.googleapis.com \ storage.googleapis.comGive additional permissions to the
bm-gcrservice account. Adding the permissions means you don't need to create multiple service accounts for individual services.gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:bm-gcr@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/gkehub.connect" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:bm-gcr@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/gkehub.admin" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:bm-gcr@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/logging.logWriter" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:bm-gcr@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/monitoring.metricWriter" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:bm-gcr@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/monitoring.dashboardEditor" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:bm-gcr@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/stackdriver.resourceMetadata.writer" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:bm-gcr@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/opsconfigmonitoring.resourceMetadata.writer"
Create a cluster configuration file
Download the
bmctlcommand line utility.mkdir baremetal && cd baremetal gcloud storage cp gs://anthos-baremetal-release/bmctl/1.33.200-gke.70/linux-amd64/bmctl . chmod a+x bmctl sudo mv bmctl /usr/local/sbin/Create a cluster configuration file for your cluster:
bmctl create config -c CLUSTER_NAMEUpdate the configuration file for use with OpenStack:
cat > bmctl-workspace/CLUSTER_NAME/CLUSTER_NAME.yaml << EOB --- gcrKeyPath: /home/abm/bm-gcr.json sshPrivateKeyPath: /home/abm/.ssh/id_rsa gkeConnectAgentServiceAccountKeyPath: /home/abm/bm-gcr.json gkeConnectRegisterServiceAccountKeyPath: /home/abm/bm-gcr.json cloudOperationsServiceAccountKeyPath: /home/abm/bm-gcr.json --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: openstack-cluster-ns --- apiVersion: baremetal.cluster.gke.io/v1 kind: Cluster metadata: name: CLUSTER_NAME namespace: openstack-cluster-ns annotations: baremetal.cluster.gke.io/external-cloud-provider: "true" spec: type: hybrid anthosBareMetalVersion: 1.33.200-gke.70 gkeConnect: projectID: PROJECT_ID controlPlane: nodePoolSpec: clusterName: CLUSTER_NAME nodes: - address: 10.200.0.11 clusterNetwork: pods: cidrBlocks: - 192.168.0.0/16 services: cidrBlocks: - 10.96.0.0/20 loadBalancer: mode: manual ports: controlPlaneLBPort: 443 vips: controlPlaneVIP: 10.200.0.101 ingressVIP: 10.200.0.102 clusterOperations: location: us-central1 projectID: PROJECT_ID storage: lvpNodeMounts: path: /mnt/localpv-disk storageClassName: node-disk lvpShare: numPVUnderSharedPath: 5 path: /mnt/localpv-share storageClassName: standard nodeAccess: loginUser: abm --- apiVersion: baremetal.cluster.gke.io/v1 kind: NodePool metadata: name: node-pool-1 namespace: openstack-cluster-ns spec: clusterName: CLUSTER_NAME nodes: - address: 10.200.0.12 EOB
Create the cluster
Create the cluster:
bmctl create cluster -c CLUSTER_NAME
Running the bmctl command starts setting up a new hybrid cluster. This
includes doing preflight checks on the nodes, creating the admin and user
clusters and also registering the cluster with Google Cloud using
Connect Agent.
The whole setup can take up to 15 minutes. You see the following output as the
cluster is being created:
Please check the logs at bmctl-workspace/CLUSTER_NAME/log/create-cluster-20210926-020741/create-cluster.log
[2021-09-26 02:07:59+0000] Creating bootstrap cluster... ⠦ kind get kubeconfig --name bmctl > ~/.kube/config && k get pods --all-namespaces
[2021-09-26 02:07:59+0000] Creating bootstrap cluster... OK
[2021-09-26 02:10:48+0000] Installing dependency components... OK
[2021-09-26 02:13:42+0000] Waiting for preflight check job to finish... OK
[2021-09-26 02:15:22+0000] - Validation Category: machines and network
[2021-09-26 02:15:22+0000] - [PASSED] gcp
[2021-09-26 02:15:22+0000] - [PASSED] node-network
[2021-09-26 02:15:22+0000] - [PASSED] 10.200.0.11
[2021-09-26 02:15:22+0000] - [PASSED] 10.200.0.11-gcp
[2021-09-26 02:15:22+0000] - [PASSED] 10.200.0.12
[2021-09-26 02:15:22+0000] - [PASSED] 10.200.0.12-gcp
[2021-09-26 02:15:22+0000] Flushing logs... OK
[2021-09-26 02:15:23+0000] Applying resources for new cluster
[2021-09-26 02:15:24+0000] Waiting for cluster to become ready OK
[2021-09-26 02:25:04+0000] Writing kubeconfig file
[2021-09-26 02:25:04+0000] kubeconfig of created cluster is at bmctl-workspace/CLUSTER_NAME/CLUSTER_NAME-kubeconfig, please run
[2021-09-26 02:25:04+0000] kubectl --kubeconfig bmctl-workspace/CLUSTER_NAME/CLUSTER_NAME-kubeconfig get nodes
[2021-09-26 02:25:04+0000] to get cluster node status.
[2021-09-26 02:25:04+0000] Please restrict access to this file as it contains authentication credentials of your cluster.
[2021-09-26 02:25:04+0000] Waiting for node pools to become ready OK
[2021-09-26 02:25:24+0000] Moving admin cluster resources to the created admin cluster
[2021-09-26 02:25:53+0000] Flushing logs... OK
[2021-09-26 02:25:53+0000] Deleting bootstrap cluster...
Verify and interact with the cluster
You can find your cluster kubeconfig file on the abm-ws VM inside the
bmctl-workspace directory. To verify your deployment, complete the following
steps:
Set the
KUBECONFIGenvironment variable with the path to the cluster configuration file to runkubectlcommands on the cluster:export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/bmctl-workspace/CLUSTER_NAME/CLUSTER_NAME-kubeconfig kubectl get nodesYou should see the nodes of the cluster printed, similar to the following output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION abm-cp1 Ready control-plane,master 5m24s v1.20.5-gke.1301 abm-w1 Ready <none> 2m17s v1.20.5-gke.1301
Sign in to your cluster from Google Cloud console
To observe your workloads in the Google Cloud console, you must sign in to the cluster. For instructions and more information about signing in to your cluster, see Work with clusters from the Google Cloud console.
Clean up
You can clean up the cluster by issuing the following command in your admin
workstation (abm-ws) VM:
export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/bmctl-workspace/CLUSTER_NAME/CLUSTER_NAME-kubeconfig
bmctl reset --cluster CLUSTER_NAME
What's next?
- To install the OpenStack Cloud Provider on the newly created cluster, follow the Configure the OpenStack Cloud Provider for Kubernetes guide.
