Oracle on Google Cloud Compute provides a way for you to migrate and run your Oracle workloads on Google Cloud, at scale. You can utilize Google Cloud's secure and reliable infrastructure and virtual machines to deploy your Oracle environment. This lets you customize, configure, and manage your database environment as per your requirements, and seamlessly integrate with Google Cloud ecosystem, which includes services such as monitoring and logging.
Oracle on Google Cloud Compute supports Rehost: lift and shift type of migration, letting you move your existing on-premises Oracle databases and applications to Google Cloud with minimal disruption.
Oracle on Google Cloud Compute lets you migrate and deploy your Oracle workloads on the following Google Cloud services:
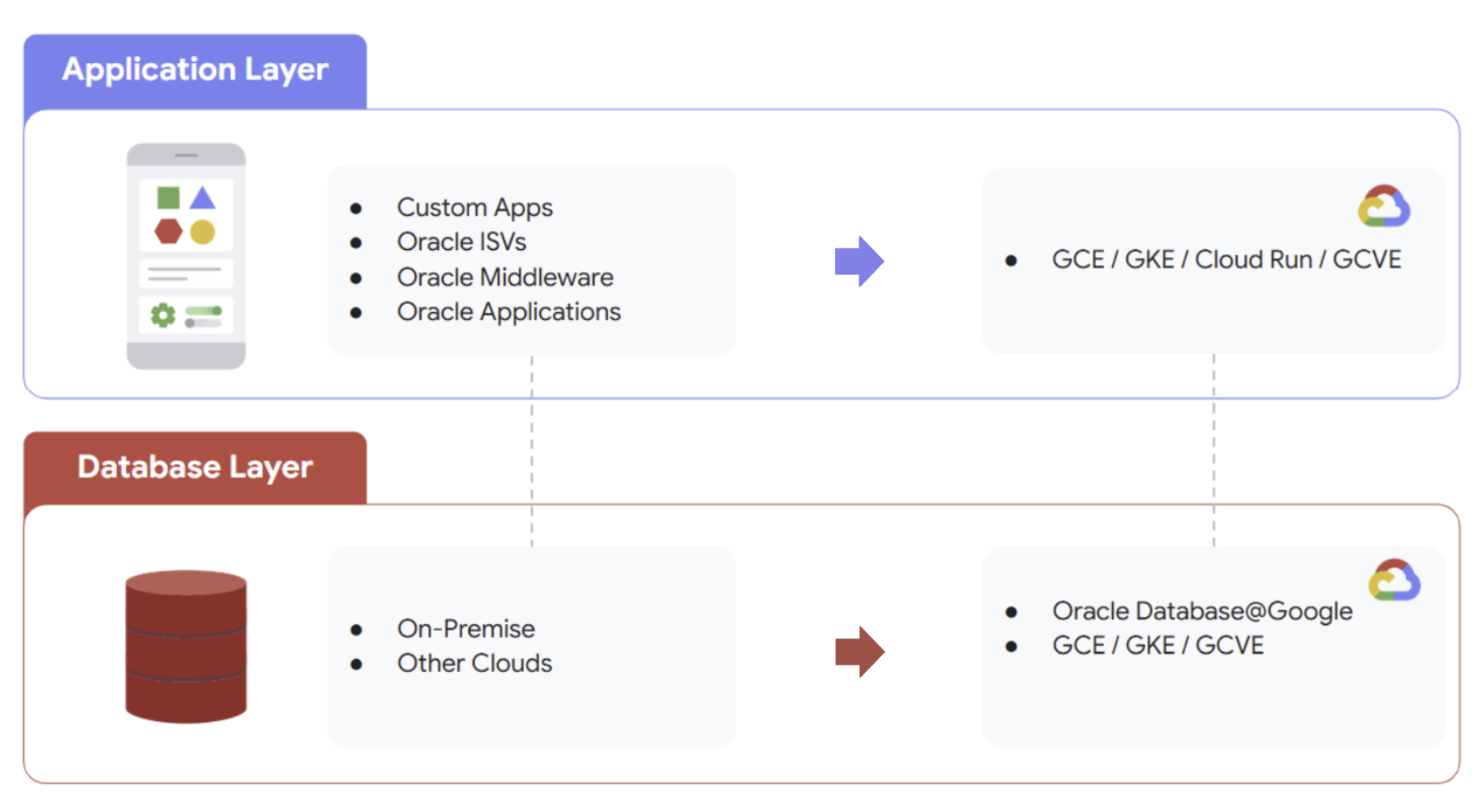
Advantages of Oracle on Google Cloud Compute
- Quick setup. You can create a VM running Oracle Linux in any region today and get started. Google Cloud VMs are quick to provision.
- Direct deployment of Oracle Databases on Google Cloud VMs. Use our Oracle Toolkit for Google Cloud to quickly deploy and manage Oracle databases on Google Cloud VMs.
- Support for all Linux operating systems that are supported by Oracle, including Oracle Linux.
- Support for Oracle technologies that you're already familiar with, such as GoldenGate and Data Guard. You can also change things up and expand to use our regional storage or managed instance groups to have multi-region disaster recovery without needing Oracle licenses on either end. It's up to you.
- Cloud-native features, such as live migration and regional storage, to enhance your deployments.
- A flexible and extensive array of machine families and scalable block storage options to choose from so that you can run a wide-range of workloads and applications that support your needs.
- Own and control your Oracle software. You get to choose the Oracle software that you want to run. If you've got an old application that still needs Oracle Database 11g, you can still run those on our latest generation of machines.
Oracle workloads on Compute Engine
Compute Engine provides the following facilities for deploying your Oracle workloads:
- Customizable infrastructure
- Choose machine types (vCPUs, RAM) based on workload needs.
- Select persistent disk storage optimized for performance.
- Run any Linux operating system that is supported by Oracle, including Oracle Linux.
- Quick deployment with Oracle Toolkit for Google Cloud
- Use Oracle Toolkit for Google Cloud software to quickly deploy and manage Oracle databases on Compute Engine VMs.
- High availability and disaster recovery
- Use Google Cloud's regional or zonal replication for redundancy.
- Implement Oracle Data Guard for failover solutions.
- Backup and recovery automate backups using Cloud Storage or Oracle RMAN.
- Performance optimization
- Use Local SSDs for high IOPS (faster transactions).
- Configure persistent disks (Standard/SSD) based on workload.
- Take advantage of Google Cloud's networking for fast data transfers.
- Licensing and cost control
- Bring Your Own License (BYOL) model.
- Optimize costs by choosing preemptible instances or committed use discounts.
- Security and compliance
- Use Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles and permissions for secure access.
- Enable VPC Service Controls for network isolation.
- Configure Oracle TDE (Transparent Data Encryption) for data security.
Get started with Oracle workloads on Compute Engine
To get started with creating and running Oracle workloads on Compute Engine, see Quickstart: Use Oracle Toolkit with Compute Engine.
Reference architectures
Following are some reference architectures for deploying Oracle workloads on Compute Engine:
- Enterprise application with Oracle Database on Compute Engine
- Enterprise application on Compute Engine VMs with Oracle Exadata in Google Cloud
- Oracle E-Business Suite with Oracle Database on Compute Engine VMs
- Oracle E-Business Suite with Oracle Exadata in Google Cloud
- Oracle PeopleSoft on Compute Engine with Oracle Exadata
Oracle on Google Kubernetes Engine
You can run an Oracle database on Google Cloud by deploying it on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), which lets you use Kubernetes for orchestration and management.
This approach involves containerizing your Oracle database and managing it as a
stateful application within a GKE cluster. To ensure data persistence and
stability, you can use a StatefulSet to manage the Oracle pods, which are backed
by PersistentVolumes using Google Cloud Persistent Disk for durable storage.
A Kubernetes Service then provides a stable network endpoint for applications to
connect to the database, enabling you to take advantage of GKE's
capabilities for high availability, scaling, and automated operations.
To simplify this process, you can use El Carro, an open source operator that automates the entire lifecycle of Oracle databases on Kubernetes. El Carro streamlines complex tasks such as initial provisioning, patching, high-availability configuration, and backup and recovery, using standard Kubernetes APIs. The Google Cloud blog post El Carro drives change for Regnology — helps drop resource requirements by almost 40 percent describes how El Carro can help an organization run business-critical Oracle databases on GKE reducing manual effort and improving operational reliability.
For a detailed walkthrough on deploying an Oracle database on GKE using an operator, refer to the tutorial Oracle Database Operator for Google Kubernetes Engine from the Oracle Developers community .
Oracle on Google Cloud VMware Engine
For information about running Oracle workloads on VMware Engine, see Support for Oracle workloads in Google Cloud VMware Engine.
Licensing
Oracle on Google Cloud Compute uses a bring your own license (BYOL) model. You are responsible for the licensing of all of your software. For more information, contact Cloud Customer Care.
