Understand the result
Enterprise Knowledge Graph writes results into a new BigQuery table for every job. This is a snapshot of the data at the time the job is executed. By default, every job generates a random cluster_id for each entity cluster. However, if you want to keep the ID stable among different job runs, use the previous BigQuery result table advanced option.
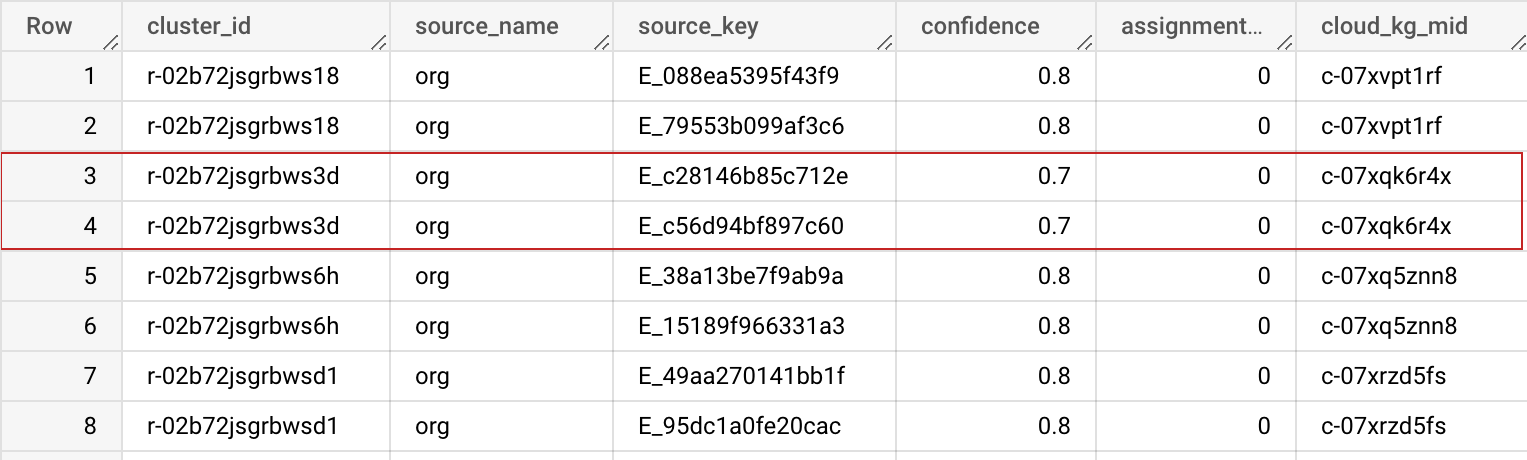
Output Schema
| Field name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cluster_id | STRING | This cluster ID is a private knowledge graph machine ID (MID) assigned to this cluster of records. It can be used to uniquely identify the record in your dataset. You can use the Previous BigQuery table in the Advanced Options to keep this cluster_id stable and consistent across multiple runs. |
| source_name | STRING | The source name specified in the input configuration, to help you join dataset together. |
| source_key | STRING | The unique key in your source table, to help you join dataset together. |
| confidence | FLOAT | Confidence score that determines how strongly these records belong to this cluster. |
| assignment_age | INTEGER | Used internally for cluster_id (MID) stabilization across different jobs. |
| cloud_kg_mid | STRING | The Google Cloud Knowledge Graph linked entity MID. You could use this MID as your permanent ID or look up additional details from Cloud Knowledge Graph API. |
Use SQL to join the dataset together
Enterprise Knowledge Graph outputs grouped entities by cluster ID. The simplest way to view the result is by using the cluster ID to "group by" your result. The following example performs a quick sanity check by joining the output table with the original table.
# get all entity clusters
SELECT distinct (cluster_id) FROM `ekg-test.<dataset>.clusters_9425187210682344597` order by cluster_id LIMIT 1000;
# join data with original table
SELECT confidence, RS., SRC. FROM `ekg-test.<dataset>.clusters_9425187210682344597` as RS join `ekg-api-test.demo.organization` as SRC
on RS.source_key = SRC.source_key where cluster_id = "r-02b72jsgrbws18";
This entity cluster represents two different records that belong to the same cluster. This same cluster_id signals that these two records should be joined and merged.

Measure success
Pair-wise
Precision: Ratio of distinct entities incorrectly identified as similar false positives (easier to detect by manual inspection).
Recall: Ratio of similar entities that aren't identified as false negatives or harder to detect.
Cluster V-measure
Cluster V-measure: (1 + beta) * homogeneity * completeness / (beta * homogeneity + completeness) where beta=1.
Cluster Homogeneity: Ratio of clusters that have entities belonging to the same entity.
Cluster Completeness: Ratio of clusters in which all entities belonging to the same entity are placed into the same cluster.
