Objetivos
Usar Dataproc Hub para crear un entorno de notebook de JupyterLab de un solo usuario que se ejecute en un clúster de Dataproc
Crear un notebook y ejecuta un trabajo de Spark en el clúster de Dataproc.
Borrar tu clúster y conserva tu notebook en Cloud Storage.
Antes de comenzar
- El administrador debe otorgarte el permiso
notebooks.instances.use(consulta Configura funciones de Identity and Access Management (IAM)).
Crea un clúster de Dataproc JupyterLab desde Dataproc Hub
Selecciona la pestaña Notebooks administrados por el usuario en la página Dataproc→Workbench de la consola de Google Cloud .
Haz clic en Abrir JupyterLab en la fila que enumera la instancia de Dataproc Hub creada por el administrador.
- Si no tienes acceso a la consola de Google Cloud , ingresa en tu navegador web la URL de la instancia de Dataproc Hub que un administrador compartió contigo.
En la página Jupyterhub→Opciones de Dataproc, selecciona una configuración y una zona del clúster. Si está habilitada, especifica las personalizaciones y, luego, haz clic en Crear.
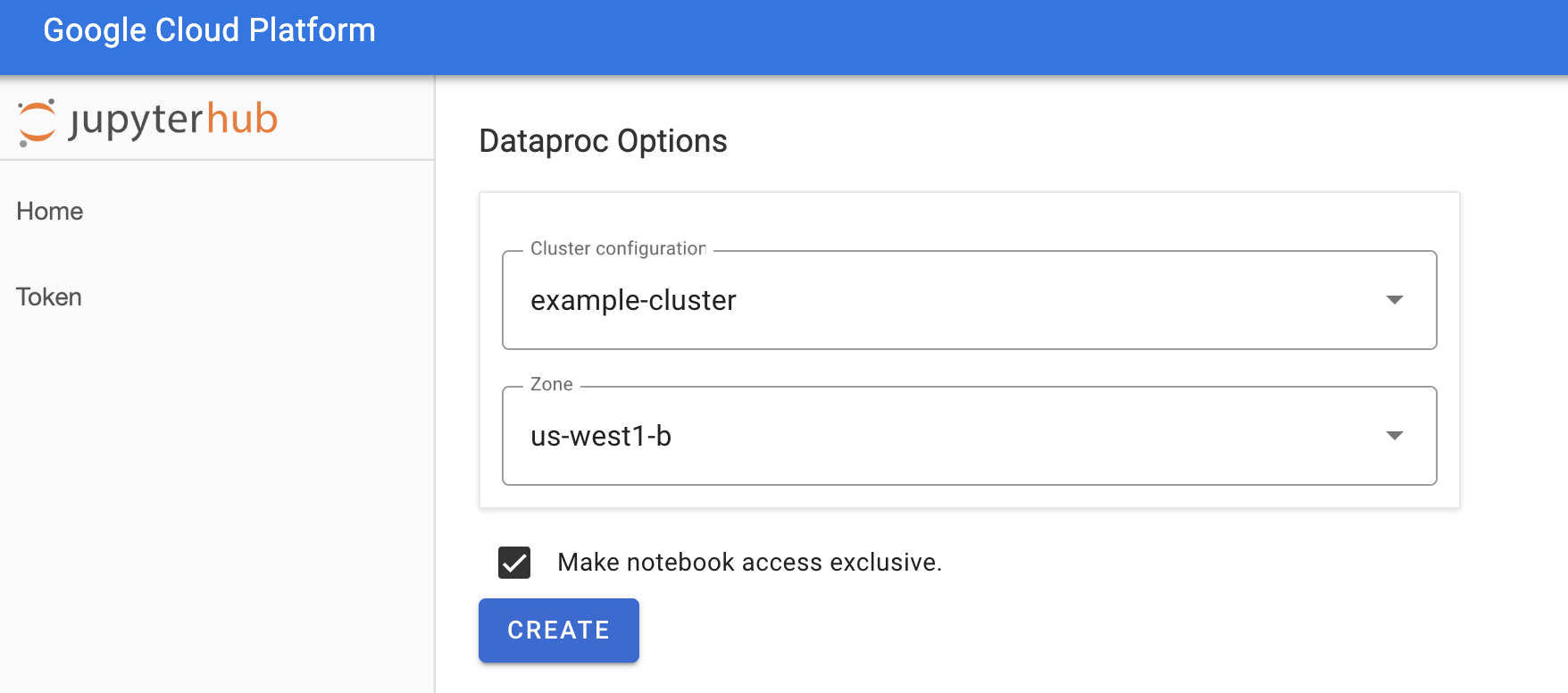
Después de crear el clúster de Dataproc, se te redireccionará a la interfaz de JupyterLab que se ejecuta en el clúster.
Crea un notebook y ejecuta un trabajo de Spark
En el panel izquierdo de la interfaz de JupyterLab, haz clic en
GCS(Cloud Storage).Crea un notebook de PySpark desde el selector de JupyterLab.
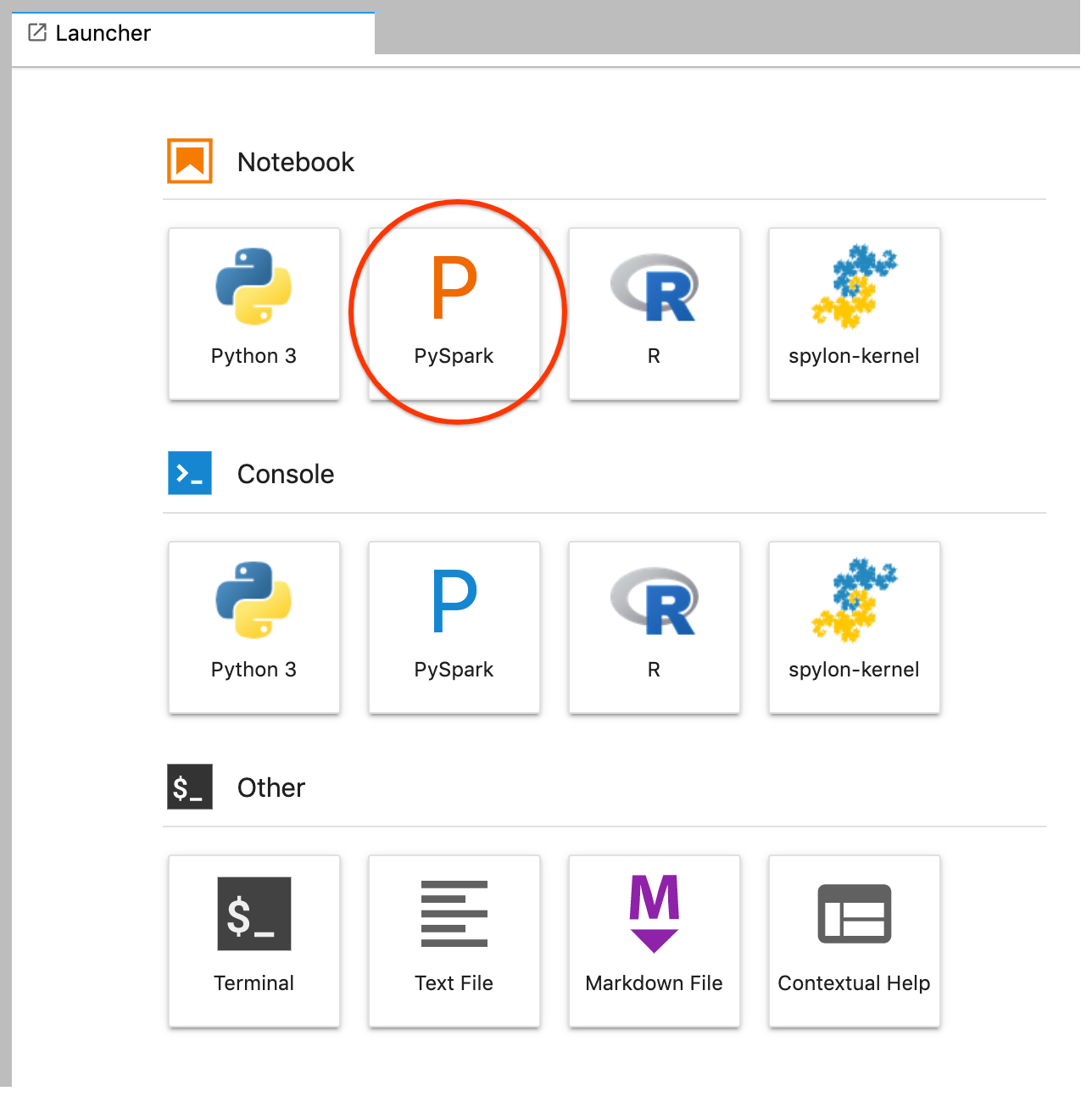
El kernel de PySpark inicializa un SparkContext (mediante la variable
sc). Puedes examinar SparkContext y ejecutar un trabajo de Spark desde el notebook.rdd = (sc.parallelize(['lorem', 'ipsum', 'dolor', 'sit', 'amet', 'lorem']) .map(lambda word: (word, 1)) .reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b)) print(rdd.collect())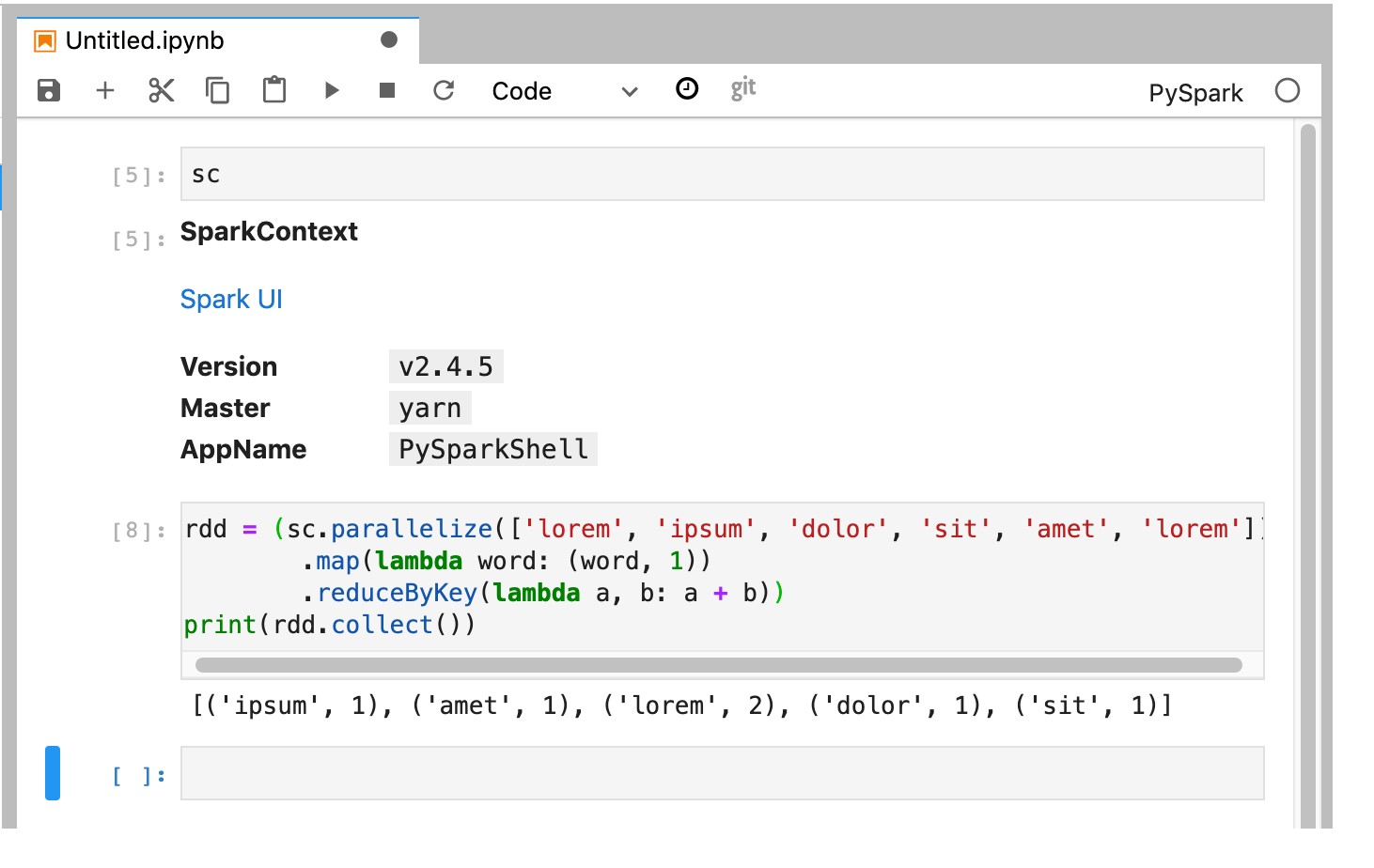
Asigna un nombre y guarda el notebook. El notebook se guarda y permanece en Cloud Storage después de que se borra el clúster de Dataproc.
Cierra el clúster de Dataproc
En la interfaz de JupyterLab, selecciona Archivo→Panel de control de Hub para abrir la página Jupyterhub.
Haz clic en Detener mi clúster para cerrar (borrar) el servidor de JupyterLab, que borra el clúster de Dataproc.
¿Qué sigue?
- Explora Spark y Jupyter Notebooks en Dataproc en GitHub.

