Conversion workspaces aggregate all conversion issues into groups and categories to help you plan for fixing conversion errors and warnings. Each category represents the type of work you might need to perform to fix the issues (review, refactor, adjust data types). Groups provide further aggregation, as they differentiate between specific cases at a lower level:
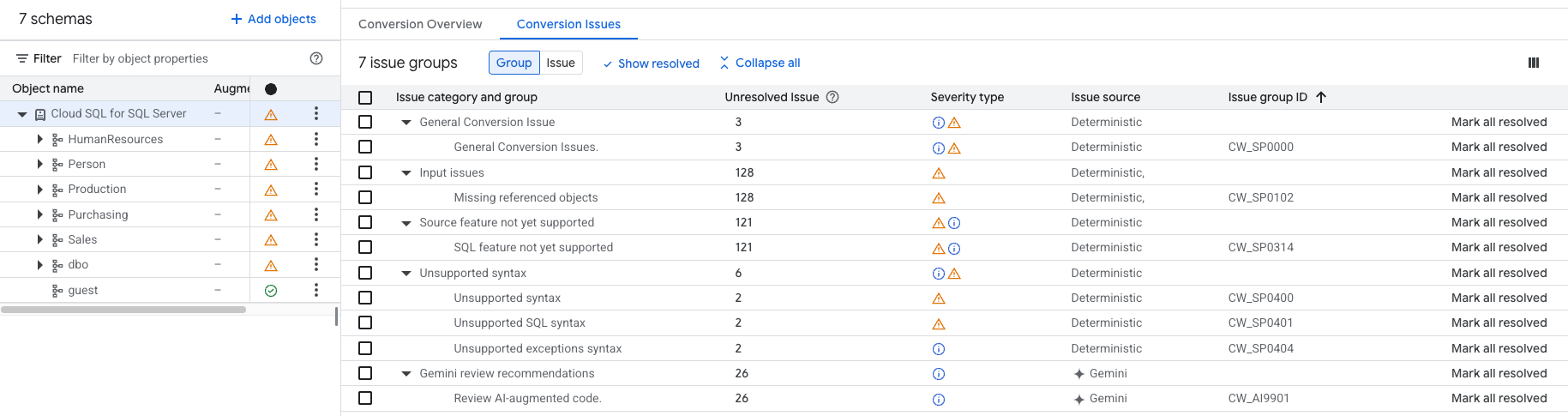

The following table lists all conversion issue groups you can encounter during schema conversion:
| Issue group ID | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Input issues (
|
|||
CW_SP0101 |
Invalid source code |
||
|
Potential root cause Errors in this group often occur when Database Migration Service encounters unknown syntax, or when the SQL Server source code isn't valid. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Correct the invalid objects in the source SQL Server database. Then, refresh the source schema snapshot in Database Migration Service and re-try the schema conversion process. Alternatively, you can exclude the object from the migration. |
|||
CW_SP0102 |
Missing referenced objects |
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service uses metadata of objects in the source tree to improve the code conversion quality of dependent objects. If your code refers to objects that aren't included in the source schema, you might experience conversion issues because Database Migration Service can't determine the structure or data types for the missing referenced columns, attributes, or objects. |
|||
| Possible mitigation
Ensure that all objects you depend on in the migrated code are included in the source tree. You can add the referenced objects to the Database Migration Service source tree, or manually adjust the references in the PostgreSQL code based on your knowledge of the source data model. If your object refers to an object in another database and uses the three-part entity name, refactor your queries to account for the differences in how SQL Server code and PostgreSQL handle three-part names. Consider the following approaches:
|
|||
CW_SP0103 |
Missing primary key |
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service requires all tables to have a primary key. For tables
without primary keys, Database Migration Service adds a string (hash) column
named |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
You can either retain or remove the |
|||
Source functionality not supported (
|
|||
CW_SP0200 |
Source functionality not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause You might be using built-in SQL Server functionality that isn't supported. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Find similar functionality in PostgreSQL and modify the converted code accordingly. We recommend that you explore Gemini-powered auto-conversion features for expediting such fixes. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
CW_SP0201 |
SQL Server system view not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause
Database Migration Service doesn't support certain SQL Server system views.
For example, you might receive this error for system views related to schema information,
such as |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Consider creating an extension in PostgreSQL to provide the missing system view. |
|||
CW_SP0202 |
SQL Server SQL function not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause
Some SQL Server built-in functions are unsupported by Database Migration Service
for conversion.
Certain functions might have their equivalents in PostgreSQL
(for example, |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Inspect which SQL Server function raised the error.
|
|||
CW_SP0203 |
SQL Server object not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause Some SQL Server built-in objects are unsupported or only partially supported by Database Migration Service for conversion. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Try to adjust your converted code to replicate the unsupported functionality:
|
|||
Source feature not supported (
|
|||
CW_SP0300 |
Source feature not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause
This group captures all generic issues that relate to SQL Server features that aren't supported for conversion. Issues in this group don't fall under any other, more specific, issue groups. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Identify the specific SQL Server feature that triggers the error.
|
|||
CW_SP0302 |
T-SQL feature not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause
This group captures all generic issues that relate to T-SQL features that aren't supported for conversion. Issues in this group don't fall under any other, more specific, issue groups. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Review and examine the unsupported T-SQL feature that raised the error. Adjust the code based on your knowledge of the T-SQL feature and behavior. You can also explore Gemini-enhanced conversion assistance. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
CW_SP0306 |
Dynamic SQL options not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service has partial support for dynamic SQL conversion.
SQL Server |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
You need to modify the converted code to match your requirements. We highly recommend that you use Gemini-powered conversion assistance to handle dynamic SQL. |
|||
CW_SP0308 |
JSON not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause
Database Migration Service code conversion doesn't support SQL Server JSON functions such as |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
You can rewrite the code to avoid the use of JSON functions or create User-Defined Functions (UDFs) to handle JSON data. Use Gemini-enhanced conversion assistance. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
CW_SP0309 |
Locking and transactions issues |
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service code conversion doesn't support the conversion of |
|||
Possible mitigation
|
|||
CW_SP0310 |
XML not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service doesn't support SQL Server XML features for conversion. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
You must manually convert the XML code in your PostgreSQL schema. |
|||
CW_SP0311 |
|
||
|
Potential root cause The SQL |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Modify the converted code to achieve functionally equivalent result. For example, you can:
|
|||
CW_SP0312 |
|
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service doesn't support the |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
You can achieve
You can create
|
|||
CW_SP0313 |
ALTER statement option not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service doesn't support |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Replace the SQL Server |
|||
CW_SP0314 |
SQL feature not supported |
||
|
Potential root cause
This group captures all generic issues that relate to SQL features that aren't supported for conversion. Issues in this group don't fall under any other, more specific, issue groups. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Adjust the converted code to cover your requirements. You can explore Gemini-powered auto-conversion features to adjust the code. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
Unsupported syntax (
|
|||
CW_SP0400 |
Unsupported syntax |
||
|
Potential root cause
This group captures all generic issues that relate to unsupported SQL or T-SQL syntax. Issues in this group don't fall under any other, more precise, issue groups. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
We recommend that you review the converted code based on your knowledge of the source syntax and behavior, and adjust the converted code. You can also explore Gemini-enhanced conversion assistance. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
CW_SP0401 |
Unsupported SQL syntax |
||
|
Potential root cause Your source code uses SQL syntax or elements that are unsupported by Database Migration Service. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
We recommend that you review the converted code based on your knowledge of the source syntax and behavior, and adjust the converted code. You can also explore Gemini-enhanced conversion assistance. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
CW_SP0402 |
Unsupported T-SQL syntax |
||
|
Potential root cause Your source code uses T-SQL syntax or elements that are unsupported by Database Migration Service. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
We recommend that you review the converted code based on your knowledge of the source syntax and behavior, and adjust the converted code. You can also explore Gemini-enhanced conversion assistance. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
CW_SP0403 |
Unsupported date and timestamp syntax |
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service might raise errors or warnings for unsupported date or timestamp syntax, operations, or expressions, for example in comparisons between mismatched data types. For more information on supported objects and data types, see About conversion workspaces. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
You can re-create most date and timestamp expressions using PostgreSQL equivalents. We recommend that you explore Gemini-powered auto-conversion features for expediting such fixes. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
CW_SP0404 |
Unsupported exceptions syntax |
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service doesn't support some elements of SQL Server exception handling syntax. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
You must manually resolve these issues in the converted code. We recommend that you explore Gemini-powered auto-conversion features for expediting such fixes. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
CW_SP0405 |
Unsupported collation syntax |
||
|
Potential root cause In SQL Server, the |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Inspect the If you need to adjust the code, for newer PostgreSQL versions
you can try the
|
|||
Data types and conversion (
|
|||
CW_SP0500 |
Data types and conversion issues |
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service can group conversion issues based on
the context (for example,
conversion issues that occur in type comparison expressions).
The |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
In most cases, Database Migration Service emits an
|
|||
CW_SP0501 |
Date format model issues |
||
|
Potential root cause
You might encounter warnings or errors when converting date or timestamp
expressions to or from strings based on a format model.
You might also see these issues if your
data is likely to be affected by the differences between how
SQL Server
The format model in SQL Server is determined by the |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Review and validate the converted PostgreSQL expressions in the conversion workspace. |
|||
CW_SP0502 |
Numeric format model issues |
||
|
Potential root cause You might encounter issues or warnings with code that converts strings
to numbers based on SQL Server format models.
You might also see this issue if your
data is likely to be affected by the differences between how
SQL Server
|
|||
|
Possible mitigation
For format models that have no equivalent in PostgreSQL, you might need to refactor your expressions or format models. We recommend that you explore Gemini-powered auto-conversion features for expediting such fixes. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
CW_SP0503 |
Casting issues |
||
|
Potential root cause You might encounter errors due to unsupported or inaccurate data type casting. This is usually because of missing or incomplete metadata. Database Migration Service might not have enough information to cast a type, for example in function arguments or procedure parameters. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Adjust the PostgreSQL code to ensure correct data type conversions. These corrections require that you are familiar with your referenced attributes, variables, and columns. |
|||
CW_SP0504 |
Comparison issues |
||
|
Potential root cause
Database Migration Service might not have enough metadata or information about data
types when converting data comparison expressions. For example, this can
happen when a user-defined type (UDT) is compared with |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Review the converted PostgreSQL expressions and resolve the issues. We recommend that you explore Gemini-powered auto-conversion features for expediting such fixes. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
Potential functional nuances (
|
|||
|
Issues in this category represent cases where your source code is correctly converted to the closest PostgreSQL equivalent, but the resulting code might behave in unexpected ways. This happens because of the functional differences in how SQL Server and PostgreSQL handle data types, formats, or objects. At first glance, this category might appear to overlap with issues in the
Data types and conversion ( |
|||
CW_SP0601 |
Review date format model |
||
|
Potential root cause Most SQL Server date and timestamp format models have appropriate equivalents in PostgreSQL, so the converted code has no semantic or functional differences. Some format models don't have an exact match, and their behavior varies. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Review and validate expressions with format model conversions to make sure that the converted code behaves as expected. |
|||
CW_SP0602 |
Review numeric format model |
||
|
Potential root cause Most source numeric format models have an equivalent in PostgreSQL, and the converted code therefore has no semantic or functional differences. However, some format models might have no exact match or behave slightly differently. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Review and validate expressions with format model conversions to make sure that the converted code works as expected. |
|||
CW_SP0604 |
Review exception message |
||
|
Potential root cause If you use the SQL Server |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
If your application, support infrastructure, or documentation depends on the error text or error number, a review of the conversion is recommended. Otherwise, you can ignore this message. |
|||
Functional review recommended (
|
|||
CW_SP0701 |
Functional review recommended |
||
|
Potential root cause
This group captures all generic issues that relate to potential functional differences in SQL Server and PostgreSQL code. Issues in this group don't fall under any other, more specific, issue groups. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
We recommend that you review the converted code based on your knowledge of the source database behvaior, and adjust the code as needed. You can also explore Gemini-powered auto-conversion features for expediting your fixes. For more information, see Convert SQL Server code and schema with Gemini assistance. |
|||
Refactoring required (
|
|||
CW_SP0802 |
Database links refactoring required |
||
|
Potential root cause Database Migration Service doesn't support the conversion of SQL Server linked servers. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
Refactor the converted code to achieve similar functionality in your
destination database. One possible approach is to re-create your
database links with the
|
|||
CW_SP0807 |
Synonyms |
||
|
Potential root cause PostgreSQL doesn't support synonyms. For code objects, Database Migration Service automatically replaces synonym references with their source schema and object name. |
|||
|
Possible mitigation
For synonym usage outside of code objects, you can use the PostgreSQL
If the synonym object refers to an object in another database and uses the three-part entity name, refactor your queries to account for the differences in how SQL Server code and PostgreSQL handle three-part names. Consider the following approaches:
|
|||
General conversion issues (
|
|||
CW_SP0000 |
General conversion issues |
||
| Potential root cause
This group contains all issues that don't fall under any other, more precise, issue categories or groups. |
|||
| Possible mitigation
We recommend that you review the converted code based on your knowledge of the source data model and database behavior, and adjust the code as needed. |
|||
CW_SP0001 |
Metadata conversion issues |
||
| Potential root cause:
This group captures all metadata-tracking issues that don't fall under any other, more specific, issue groups. |
|||
| Possible mitigation:
Examples of issues in this group are usually related to compilation errors or warnings that can lead to problems with data types in the converted PostgreSQL. We recommend that you review the converted code based on your knowledge of the source database behavior and adjust the faulty references. |
|||
CW_SP0002 |
Contact your support team |
||
Potential root cause In special edge cases, you might encounter an internal error with a valid SQL Server source object. If you do, contact your support team for additional assistance. |
|||
