On Compute Engine you can manage the operating systems that are running on your virtual machines (VMs) by using VM Manager.
You can enable VM Manager for individual VMs, or for a project, or for all projects in a folder or organization. To review the steps needed to set up your VMs to use VM Manager, see Setup overview.
After setting up VM Manager, you can view audit logs for API operations performed with the OS Config API, see Viewing VM Manager audit logs.
Before you begin
- Review OS Config quotas for your project.
-
If you haven't already, set up authentication.
Authentication verifies your identity for access to Google Cloud services and APIs. To run
code or samples from a local development environment, you can authenticate to
Compute Engine by selecting one of the following options:
Select the tab for how you plan to use the samples on this page:
Console
When you use the Google Cloud console to access Google Cloud services and APIs, you don't need to set up authentication.
gcloud
-
Install the Google Cloud CLI. After installation, initialize the Google Cloud CLI by running the following command:
gcloud initIf you're using an external identity provider (IdP), you must first sign in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
- Set a default region and zone.
REST
To use the REST API samples on this page in a local development environment, you use the credentials you provide to the gcloud CLI.
Install the Google Cloud CLI. After installation, initialize the Google Cloud CLI by running the following command:
gcloud initIf you're using an external identity provider (IdP), you must first sign in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
For more information, see Authenticate for using REST in the Google Cloud authentication documentation.
-
Supported operating systems
For the full list of operating system versions that support VM Manager, see Operating system details. If the OS config agent is not available for a particular operating system, you cannot enable VM Manager for a VM that runs this operating system.
Enable VM Manager using an organization policy
You can automatically enable VM Manager for all new VMs in your organization, folder, or project by using the Require OS Config organization policy.
When the Require OS Config boolean constraint is set up, the following conditions are applied:
enable-osconfig=TRUEis included in the project metadata for all new projects.- Requests that set
enable-osconfigtoFALSEin instance or project metadata are rejected, for new and existing VMs and projects. - This organization policy does not change the
enable-osconfigmetadata value toTRUEfor VMs or for the projects that were created before enabling the policy. If you want to enable VM Manager on those VMs or projects, we recommend that you update the metadata. For more information, see Set the metadata values.
When the OS Config organization policy is enabled, you can still use the
osconfig-disabled-features metadata to disable one or more VM Manager features.
Enable OS Config organization policy
To enable the OS Config policy, you can set the Require OS Config constraint on the entire organization, folders, or specific projects by using either the Google Cloud console or the Google Cloud CLI.
Console
To set the OS Config organization policy from the console, complete the following steps:
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Organization policies page.
From the project picker, select the project, folder, or organization for which you want to edit organization policies.
The Organization policies page displays a filterable list of organization policy constraints that are available.
Select Require OS Config constraint from the list of constraints. The Policy details page that appears describes the constraint and provides information about how the constraint is applied.
To update the organization policy for this resource, click Manage policy.
On the Edit policy page, select Override parent's policy.
Select Add a rule.
Under Enforcement, select whether enforcement of this organization policy should be on.
To enforce the policy, click Set policy.
gcloud
To set the OS Config organization policy, use the
gcloud beta resource-manager org-policies enable-enforce
command.
Find your organization ID.
gcloud organizations list
Set the constraint in your organization. Replace
organization-idwith your your organization ID.gcloud beta resource-manager org-policies enable-enforce compute.requireOsConfig \ --organization=organization-id
You can also apply the OS Config organization policy to a folder or a project
with the --folder or the --project flags, and the folder ID and project
ID, respectively.
For folders, run the following command:
gcloud beta resource-manager org-policies enable-enforce compute.requireOsConfig \
--folder=folder-id
For projects, run the following command:
gcloud beta resource-manager org-policies enable-enforce compute.requireOsConfig \
--project=project-id
Replace the following:
folder-id: your folder ID.project-id: your project ID.
Enable VM Manager in a project
To enable VM Manager in your project, you have two options:
- Automatic enablement: applies to your entire Google Cloud project. You complete automatic enablement from the Google Cloud console. You might still need to manually complete some steps.
Manual enablement: can be done per VM or for the entire Google Cloud project.
Manual
To manually set up VM Manager, complete the following steps:
- In your Google Cloud project, enable the OS Config API.
- On each VM, check if the OS Config agent is installed. If the agent is not already installed, install the OS Config agent.
- On either your project or on each VM, set instance metadata for the OS Config agent. This step is needed to make the OS Config agent active in your VM or project.
- Verify that all VMs have an attached service account. You don't need to grant any IAM roles to this service account. VM Manager uses this service account to sign requests to the API service.
- If your VM is running within a private VPC network and does not have public internet access, enable Private Google Access.
- If you use HTTP proxy for your VMs, configure an HTTP proxy.
- Optional. On either your project or on each VM, disable the features that you don't need.
Automatic
The first time you navigate to any of the VM Manager pages in the Google Cloud console, you can choose to automatically enable VM Manager.
If you follow the guided steps, you can use the automatic enablement to complete the following:
- Enable VM Manager (OS Config API) on the Google Cloud project
- Activate OS Config agents on all VMs in the Google Cloud project that have the agent installed
Enable the OS Config service API
In your Google Cloud project, enable the OS Config API.
Console
In the Google Cloud console, enable VM Manager (OS Config API).
gcloud
To enable the API run the following command:
gcloud services enable osconfig.googleapis.com
Check if the OS Config agent is installed
The OS Config agent is installed by default on CentOS, Container-Optimized OS (COS),
Debian, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), Rocky Linux, SLES, Ubuntu, and
Windows Server images that have a build date of v20200114 or later.
For information about the versions of operating systems with the
OS Config agent installed, see
Operating system details.
These agents run idly until you enable the agent metadata,
and enable the service API.
Linux
To check whether your Linux VM has the agent installed, run the following command:
sudo systemctl status google-osconfig-agent
If the agent is installed and running, the output resembles the following:
google-osconfig-agent.service - Google OSConfig Agent
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/google-osconfig-agent.service; enabled; vendor preset:
Active: active (running) since Wed 2020-01-15 00:14:22 UTC; 6min ago
Main PID: 369 (google_osconfig)
Tasks: 8 (limit: 4374)
Memory: 102.7M
CGroup: /system.slice/google-osconfig-agent.service
└─369 /usr/bin/google_osconfig_agent
If the agent is not installed, install the OS Config agent.
Windows
To check whether your Windows VM has the agent installed, run the following command:
PowerShell Get-Service google_osconfig_agent
If the agent is installed and running, the output resembles the following:
Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running google_osconfig... Google OSConfig Agent
If the agent is not installed, install the OS Config agent.
Install the OS Config agent
Before you follow these steps to install the agent, check if the agent is already running on your VM.
On each VM, install the OS Config agent. You can install the OS Config agent by using one of the following options:
- Install the agent manually from the terminal.
- Use a startup script on your VMs.
- Automate the installation of OS Config on multiple VMs by using a Google Cloud Observability agent policy.
- Install Ops Agent during VM creation.
Install the agent manually
Use this option to install the OS Config agent on an existing VM.
To install the agent, complete the following steps:
Connect to the VM that you want to install the OS Config agent on.
Install the OS Config agent.
Windows Server
To install the OS Config agent on a Windows server, run the following command:
googet -noconfirm install google-osconfig-agent
Ubuntu
To install the OS Config agent on an Ubuntu VM, run the following commands:
Set up the Ubuntu repository.
For Ubuntu 20.04 and later versions, run the following commands:
Add the Ubuntu repository.
sudo su -c "echo 'deb http://packages.cloud.google.com/apt google-compute-engine-focal-stable main' > \ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-compute-engine.list"
Import the Google Cloud public key.
curl https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | \ sudo apt-key add -
For Ubuntu 18.04 and later versions, run the following commands:
Add the Ubuntu repository.
sudo su -c "echo 'deb http://packages.cloud.google.com/apt google-compute-engine-bionic-stable main' > \ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-compute-engine.list"
Import the Google Cloud public key.
curl https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | \ sudo apt-key add -
For Ubuntu 16.04, run the following commands:
Add the Ubuntu repository.
sudo su -c "echo 'deb http://packages.cloud.google.com/apt google-compute-engine-xenial-stable main'> \ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-compute-engine.list"
Import the Google Cloud public key.
curl https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | \ sudo apt-key add -
Install the OS Config agent.
sudo apt update sudo apt -y install google-osconfig-agent
Debian
To install the OS Config agent on a Debian VM, run the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt -y install google-osconfig-agent
Adding the Google Cloud repository and public key
If you are using a VM instance that was not created from a Google-provided image or got a "unable to locate package" error message, complete the following steps to add the Google Cloud repository and import the public key.
After you add the repository and import the key, you can then run the commands to install the OS Config agent.
Set up the Debian Cloud repository:
Debian 13 and later
Install the public repository GPG key to
/etc/apt/keyrings:sudo curl https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/google-keyring.gpgDetermine the Debian distro name. Then, create the source list file,
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-cloud.list:eval $(grep VERSION_CODENAME /etc/os-release) sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-cloud.list << EOM deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/google-keyring.gpg] http://packages.cloud.google.com/apt google-compute-engine-${VERSION_CODENAME}-stable main EOM
Debian 12 and earlier
Install the public repository GPG key:
curl https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -Determine the Debian distro name. Then, create the source list file,
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-cloud.list:eval $(grep VERSION_CODENAME /etc/os-release) sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-cloud.list << EOM deb http://packages.cloud.google.com/apt google-compute-engine-${VERSION_CODENAME}-stable main deb http://packages.cloud.google.com/apt google-cloud-packages-archive-keyring-${VERSION_CODENAME} main EOM
RHEL/CentOS/Rocky
To install the OS Config agent on a RHEL 7/8, CentOS 7/8 VM or Rocky Linux 8/9, run the following command:
sudo yum -y install google-osconfig-agent
SLES/openSUSE
To install the OS Config agent on a SLES or openSUSE VM, run the following commands:
Set up the SLES repository.
For SLES 12, run the following command:
sudo su -c "cat > /etc/zypp/repos.d/google-compute-engine.repo <<EOM [google-compute-engine] name=Google Compute Engine baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/google-compute-engine-sles12-stable enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOM"
For SLES 15 and OpenSUSE 15, run the following command:
sudo su -c "cat > /etc/zypp/repos.d/google-compute-engine.repo <<EOM [google-compute-engine] name=Google Compute Engine baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/google-compute-engine-sles15-stable enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOM"
Import the GPG keys for Google Cloud.
sudo rpm --import https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg \ --import https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
Install the OS Config agent.
sudo zypper -n --gpg-auto-import-keys install --from google-compute-engine google-osconfig-agent
Install the agent using a startup script
You can also use the manual installation commands to create a startup script that installs the OS Config agent during VM creation.
- Copy the manual commands for your operating system.
Provide the startup script to your VM creation method.
For example, if you are using the
gcloud compute instances createcommand to create a Debian 10 VM, your command resembles the following:gcloud compute instances create VM_NAME \ --image-family=debian-10 --image-project=debian-cloud \ --metadata startup-script='#! /bin/bash apt update apt -y install google-osconfig-agent'
Replace
VM_NAMEwith the name of your VM.Verify that the startup script completes. To verify whether the startup script completes, review the logs or check the serial console.
Set the metadata values
You can either set instance metadata on each VM or project metadata that applies to all VMs in your project.
On your Google Cloud project or VM, set the enable-osconfig metadata value
to TRUE. Setting the enable-osconfig metadata value to TRUE enables the
following:
- Patch
- OS policies
- OS inventory management
- For the earlier version of OS inventory management, you must also
set the
enable-guest-attributesmetadata value toTRUE. If both metadata values are not set, the dashboard showsno datafor the VM. This is not needed for the later version. For information about the two OS inventory management versions, see OS inventory management versions.
- For the earlier version of OS inventory management, you must also
set the
Console
You can apply the metadata values on your Google Cloud projects or VMs using one of the following options:
Option 1: Set
enable-osconfigin project-wide metadata, so that it applies to all of the VMs in your project.In the Google Cloud console, go to the Metadata page.
Click Edit.
Add the following metadata entry:
Key:
enable-osconfig
Value:TRUEFor the earlier version of OS inventory management, set both
enable-osconfigandenable-guest-attributes:- Key:
enable-osconfig
Value:TRUE - Key:
enable-guest-attributes
Value:TRUE
- Key:
Click Save to apply the changes.
Option 2: Set
enable-osconfigin VM metadata when you create an instance.In the Google Cloud console, go to the Create an instance page.
Specify the VM details.
Expand the Advanced options section, and do the following:
- Expand the Management section.
In the Metadata section, click Add item and add the following metadata entries:
Key:
enable-osconfig
Value:TRUE.For the earlier version of OS inventory management, set both
enable-osconfigandenable-guest-attributes:- Key:
enable-osconfig
Value:TRUE - Key:
enable-guest-attributes
Value:TRUE
- Key:
To create the VM, click Create.
Option 3: Set
enable-osconfigin metadata of an existing VM.In the Google Cloud console, go to the VM instances page.
Click the name of the VM for which you want to set the metadata value.
On the Instance details page, click Edit to edit the settings.
Under Custom metadata, add the following metadata entries:
Key:
enable-osconfig
Value:TRUE.For the earlier version of OS inventory management, set both
enable-osconfigandenable-guest-attributes:- Key:
enable-osconfig
Value:TRUE - Key:
enable-guest-attributes
Value:TRUE
- Key:
Click Save to apply your changes to the VM.
gcloud
Use the
project-info add-metadata
or the
instances add-metadata command
with the --metadata=enable-osconfig=TRUE flag.
You can apply the metadata values on your projects or VMs using one of the following options:
Option 1: Set
enable-osconfigin project-wide metadata, so that it applies to all of the instances in your project:gcloud compute project-info add-metadata \ --project PROJECT_ID \ --metadata=enable-osconfig=TRUE
For the earlier version of OS inventory management, set both
enable-osconfigandenable-guest-attributes:gcloud compute project-info add-metadata \ --project PROJECT_ID \ --metadata=enable-guest-attributes=TRUE,enable-osconfig=TRUE
Replace
PROJECT_IDwith your project ID.Option 2: Set
enable-osconfigin metadata of an existing instance.gcloud compute instances add-metadata VM_NAME \ --metadata=enable-osconfig=TRUE
For the earlier version of OS inventory management, set both
enable-osconfigandenable-guest-attributes:gcloud compute instances add-metadata VM_NAME \ --metadata=enable-guest-attributes=TRUE,enable-osconfig=TRUE
Replace
VM_NAMEwith the name of your VM.Option 3: Set
enable-osconfigin instance metadata when you create an instance.gcloud compute instances create VM_NAME \ --metadata=enable-osconfig=TRUE
For the earlier version of OS inventory management, set both
enable-osconfigandenable-guest-attributes:gcloud compute instances create VM_NAME \ --metadata=enable-guest-attributes=TRUE,enable-osconfig=TRUE
Replace
VM_NAMEwith the name of your VM.
REST
You can set the metadata value at either the Google Cloud project or instance level.
- For instructions on setting project-wide metadata, see setting project-wide custom metadata.
- For instructions on setting instance metadata, see setting instance metadata.
The following key-value pair is required as part of the metadata property:
- Key:
enable-osconfig
Value:TRUE
For the earlier version of OS inventory management, also add the following key-value pair:
- Key:
enable-guest-attributes
Value:TRUE
Configure an HTTP proxy
If you use an HTTP proxy for your VMs, run the following commands to set the
http_proxy and https_proxy environment variables.
You should also exclude the metadata server (169.254.169.254) by configuring
the no_proxy environment variable so that the OS Config agent can access the
local metadata server.
Linux
On Linux distributions that use systemd, as the root user, add the proxy
environment variables to the google-osconfig-agent.service unit:
mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/google-osconfig-agent.service.d cat >/etc/systemd/system/google-osconfig-agent.service.d/override.conf <<EOF [Service] Environment="http_proxy=http://PROXY_IP:PROXY_PORT" \ "https_proxy=http://PROXY_IP:PROXY_PORT" \ "no_proxy=169.254.169.254,metadata,metadata.google.internal" EOF
Replace PROXY_IP and PROXY_PORT
with the IP address and port number of your proxy server,
respectively.
Restart the OS Config agent service:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart google-osconfig-agent
To confirm that the variables are set correctly, check the environment variables for the running agent:
tr '\0' '\n' < /proc/$(systemctl show -p MainPID --value google-osconfig-agent)/environ
Windows
Run the following commands from an administrator command prompt.
setx http_proxy http://PROXY_IP:PROXY_PORT /m setx https_proxy http://PROXY_IP:PROXY_PORT /m setx no_proxy 169.254.169.254,metadata,metadata.google.internal /m
Replace PROXY_IP and PROXY_PORT
with the IP address and port number of your proxy server, respectively.
Google recommends that you exclude *.googleapis.com by adding the
no_proxy environment variable to avoid connection issues from the OS Config
agent. If you want to connect only specific VMs to the OS Config agent,
prefix the zone the VMs are in, and use the format [zone-name]-osconfig.googleapis.com.
For example, us-central1-f-osconfig.googleapis.com.
Disable features that you don't need
For features that you might not need, you can disable them by
setting the following metadata values:
osconfig-disabled-features=FEATURE1,FEATURE2.
Replace FEATURE1,FEATURE2 with any of
the following values:
- OS inventory management:
osinventory - Patch and OS policies:
tasks - OS guest policies (beta):
guestpolicies
Use one of the following methods to disable the metadata values.
Console
You can disable the metadata values on your Google Cloud projects or VMs by using one of the following options:
Option 1: Disable feature in project-wide metadata so that it applies to all of the instances in your project.
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Metadata page.
Click Edit.
Add the following metadata entry:
Key:
osconfig-disabled-features
Value:FEATURE1,FEATURE2For example:
Key:osconfig-disabled-features
Value:osinventory,guestpoliciesClick Save to apply the changes.
Option 2: Disable feature in metadata of an existing VM.
In the Google Cloud console, go to the VM instances page.
Click the name of the VM on which you want to set the metadata value.
On the Instance details page, click Edit to edit the VM settings.
Under Custom metadata, add the following metadata entries:
Key:
osconfig-disabled-features
Value:FEATURE1,FEATURE2For example:
Key:osconfig-disabled-features
Value:osinventoryClick Save to apply your changes to the VM.
gcloud
Use the
project-info add-metadata
or the
instances add-metadata gcloud command
with the --metadata=osconfig-disabled-features flag.
If you are disabling multiple features, the flag must have the format
--metadata=osconfig-disabled-features=FEATURE1,FEATURE2.
See example 2.
Examples
Example 1 To disable Patch at the Google Cloud project level using the Google Cloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloud compute project-info add-metadata \
--project PROJECT_ID \
--metadata=osconfig-disabled-features=tasks
Example 2 To disable OS policies and OS inventory management at the project level using the Google Cloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloud compute project-info add-metadata \
--project PROJECT_ID \
--metadata=osconfig-disabled-features=osinventory,guestpolicies
Replace PROJECT_ID with your project ID.
REST
You can set the metadata value at either the Google Cloud project or instance level.
- For instructions on setting project-wide metadata, see setting project-wide custom metadata.
- For instructions on setting instance metadata, see setting instance metadata.
The following key-value pair is required as part of the metadata property:
- Key:
osconfig-disabled-features - Value: Can be any one or a combination of the following flags:
osinventorytasksguestpolicies
Requirements for an active OS Config agent
For the OS Config agent to be considered active and billable, it must satisfy all of the following requirements:
- VM Manager must be set up.
The VM must be in
RUNNINGstate and the OS Config agent must be communicating with the OS Config service.If a VM is stopped, suspended, or disconnected from the network, the agent on that VM is not counted as an active agent.
Verify the setup
After completing the setup procedure, you can verify the setup.
View VM Manager feature settings for your project
To verify whether all VM Manager features are enabled in your project, do the following:
gcloud
Use the gcloud compute os-config project-feature-settings describe command as follows:
gcloud compute os-config project-feature-settings describe \
--project PROJECT_ID
The output of the command is similar to the following:
name: projects/my-project/locations/global/projectFeatureSettings patchAndConfigFeatureSet: OSCONFIG_C
The value OSCONFIG_C represents the full VM Manager feature set and
OSCONFIG_B represents the limited feature set.
REST
To view VM Manager features at the Google Cloud project,
create a GET request to the
projects.locations.global.getProjectFeatureSettings method.
GET https://osconfig.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/global/projectFeatureSettings
Replace PROJECT_ID with your project ID.
If successful, the method returns the project feature settings as shown in the following example:
{
"name": "projects/my-project/locations/global/projectFeatureSettings",
"patchAndConfigFeatureSet": "OSCONFIG_C"
}
The value OSCONFIG_C represents the full VM Manager feature set and
OSCONFIG_B represents the limited feature set.
Enable full VM Manager functionality
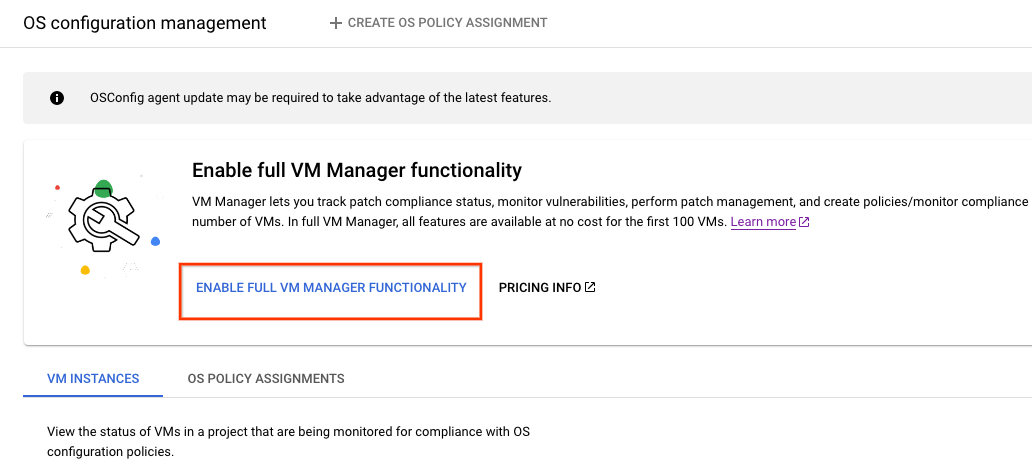
If VM Manager isn't enabled in your project and you install Ops Agent during VM creation, VM Manager is enabled in the limited mode. In this mode, VM Manager offers a subset of features for unlimited number of VMs at no cost. For example, you can view the OS policy assignments for your VMs on the OS policies page, but you cannot create or edit OS policy assignments.
To enable all VM Manager features for these VMs with Ops Agent installed, do the following:
Console
- In the Google Cloud console, go to the OS policies page.
Click Enable full VM Manager functionality to enable all VM Manager features.
gcloud
To enable all VM Manager features for the Google Cloud project,
use the
gcloud compute os-config project-feature-settings update command:
gcloud compute os-config project-feature-settings update \
--project PROJECT_ID \
--patch-and-config-feature-set=full
REST
To enable all VM Manager features at the Google Cloud project level,
send a PATCH request to the
projprojects.locations.global.updateProjectFeatureSettings method.
PATCH https://osconfig.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/global/projectFeatureSettings
{
"name": "projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/global/projectFeatureSettings",
"patchAndConfigFeatureSet": "OSCONFIG_C"
}
Replace PROJECT_ID with your project ID. The
value OSCONFIG_C represents the full VM Manager feature set.
Disable the OS Config agent
Disabling the OS Config agent does not affect the behavior of your VM. You can disable the agent the same way you stop other services of the operating system.
Linux
To disable the agent using systemctl, run the following commands:
sudo systemctl stop google-osconfig-agent sudo systemctl disable google-osconfig-agent
Windows
To disable the agent using powershell, run the following command:
PowerShell Stop-Service google_osconfig_agent [-StartupType disabled]
What's next?
- Create an OS policy assignment.
- View operating system details.
- Create patch jobs.
- Learn more about the VM Manager.
