Cloud Composer 3 | Cloud Composer 2 | Cloud Composer 1
Nesta página, descrevemos como agrupar tarefas em pipelines do Airflow usando os seguintes padrões de design:
- Agrupar tarefas no gráfico do DAG.
- Como acionar DAGs filhos de um DAG pai.
- Como agrupar tarefas com o operador
TaskGroup.
Agrupar tarefas no gráfico do DAG
Para agrupar tarefas em determinadas fases do pipeline, use as relações entre as tarefas no arquivo DAG.
Veja o exemplo a seguir.
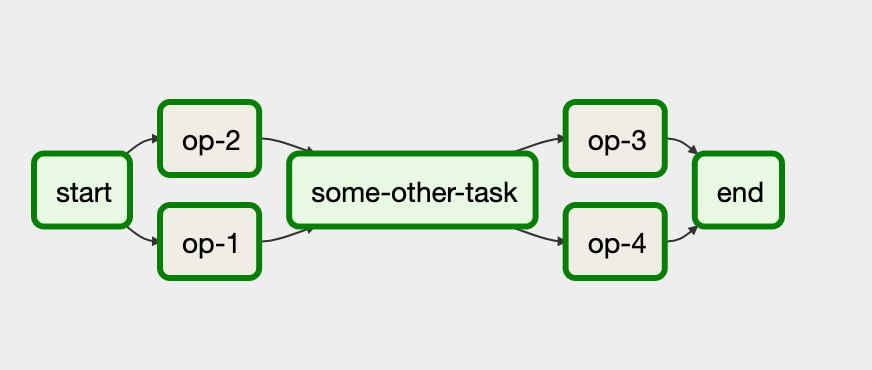
Neste fluxo de trabalho, as tarefas op-1 e op-2 são executadas juntas após a tarefa inicial start. Para isso, agrupe as tarefas com a instrução start >> [task_1, task_2].
O exemplo a seguir fornece uma implementação completa desse DAG:
Acionar DAGs filhos de um DAG pai
É possível acionar um DAG de outro com o
operador TriggerDagRunOperator.
Veja o exemplo a seguir.

Neste fluxo de trabalho, os blocos dag_1 e dag_2 representam uma série de tarefas
agrupadas em um DAG separado no ambiente do
Cloud Composer.
A implementação desse fluxo de trabalho requer dois arquivos DAG separados. O arquivo DAG de controle tem a seguinte aparência:
A implementação do DAG filho, que é acionada pelo DAG de controle, tem a seguinte aparência:
É preciso fazer upload dos dois arquivos DAG no ambiente do Cloud Composer para que o DAG funcione.
Como agrupar tarefas com o operador TaskGroup
É possível usar o operador TaskGroup para agrupar tarefas no DAG. As tarefas definidas em um bloco TaskGroup ainda fazem parte
do DAG principal.
Veja o exemplo a seguir.
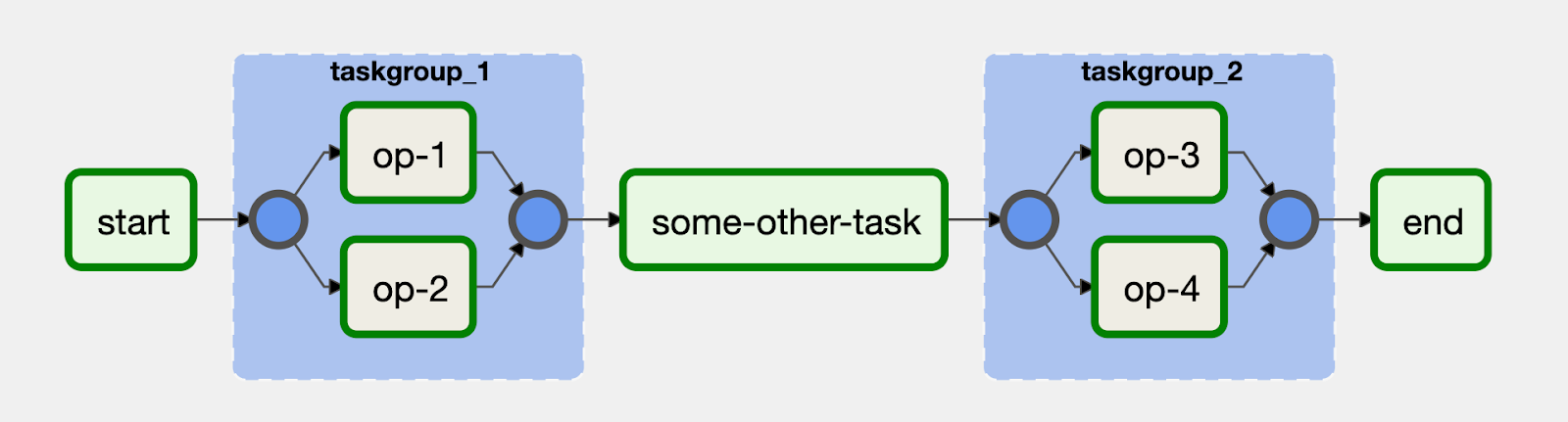
As tarefas op-1 e op-2 são agrupadas em um bloco com o ID taskgroup_1. Uma implementação desse fluxo de trabalho se parece com o seguinte código:

