Generalização é o processo de tomar um valor distinto e abstraí-lo em um valor mais geral. Esse processo tenta preservar a utilidade dos dados e, ao mesmo tempo, reduzir a capacidade de identificação deles.
Dependendo do tipo de dados, há muitos níveis de generalização. A quantidade de generalização necessária é algo a ser medido em um conjunto de dados ou em uma população do mundo real com técnicas como as incluídas nos métodos de análise de risco da proteção de dados sensíveis.
Uma técnica de generalização comum que a Proteção de dados sensíveis aceita é o agrupamento por classes. Com ela, é possível agrupar os registros em buckets menores na tentativa de minimizar o risco de um invasor associar informações confidenciais a informações de identificação. Assim, será possível reter o significado e a utilidade, mas os valores individuais que têm poucos participantes poderão ser ocultados.
Cenário de agrupamento por classes 1
Pense neste cenário de agrupamento por classes numérico: um banco de dados armazena as pontuações de satisfação dos usuários, que vão de 0 a 100. Ele tem uma aparência semelhante à seguinte:
| user_id | score |
|---|---|
| 1 | 100 |
| 2 | 100 |
| 3 | 92 |
| ... | ... |
Ao verificar os dados, você percebe que alguns valores raramente são usados pelos usuários. Na verdade, existem algumas pontuações que são mapeadas para apenas um usuário. Por exemplo, a maioria dos usuários escolhe 0, 25, 50, 75 ou 100. No entanto, cinco usuários escolheram 95 e apenas um usuário escolheu 92. Em vez de manter os dados brutos, você poderá generalizar esses valores em grupos e eliminar os grupos com poucos participantes. Dependendo da forma como os dados são usados, generalizar dessa maneira pode ajudar a evitar a reidentificação.
Opte por remover essas linhas de dados outliers ou tente preservar sua utilidade usando o agrupamento por classes. Para este exemplo, vamos agrupar por classes todos os valores de acordo com o seguinte:
- 0 a 25: "baixo"
- 26-75: "médio"
- 76 a 100: "alto"
O agrupamento por classes na Proteção de Dados Sensíveis é uma das muitas transformações primitivas disponíveis para a desidentificação. A configuração JSON a seguir ilustra como implementar esse cenário de agrupamento por classes na API DLP. Este JSON pode ser incluído em uma solicitação para o método content.deidentify:
C#
Para saber como instalar e usar a biblioteca de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis, consulte Bibliotecas de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis.
Para autenticar na Proteção de dados sensíveis, configure o Application Default Credentials. Para mais informações, consulte Configurar a autenticação para um ambiente de desenvolvimento local.
Go
Para saber como instalar e usar a biblioteca de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis, consulte Bibliotecas de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis.
Para autenticar na Proteção de dados sensíveis, configure o Application Default Credentials. Para mais informações, consulte Configurar a autenticação para um ambiente de desenvolvimento local.
Java
Para saber como instalar e usar a biblioteca de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis, consulte Bibliotecas de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis.
Para autenticar na Proteção de dados sensíveis, configure o Application Default Credentials. Para mais informações, consulte Configurar a autenticação para um ambiente de desenvolvimento local.
Node.js
Para saber como instalar e usar a biblioteca de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis, consulte Bibliotecas de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis.
Para autenticar na Proteção de dados sensíveis, configure o Application Default Credentials. Para mais informações, consulte Configurar a autenticação para um ambiente de desenvolvimento local.
PHP
Para saber como instalar e usar a biblioteca de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis, consulte Bibliotecas de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis.
Para autenticar na Proteção de dados sensíveis, configure o Application Default Credentials. Para mais informações, consulte Configurar a autenticação para um ambiente de desenvolvimento local.
Python
Para saber como instalar e usar a biblioteca de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis, consulte Bibliotecas de cliente da Proteção de dados sensíveis.
Para autenticar na Proteção de dados sensíveis, configure o Application Default Credentials. Para mais informações, consulte Configurar a autenticação para um ambiente de desenvolvimento local.
REST
...
{
"primitiveTransformation":
{
"bucketingConfig":
{
"buckets":
[
{
"min":
{
"integerValue": "0"
},
"max":
{
"integerValue": "25"
},
"replacementValue":
{
"stringValue": "Low"
}
},
{
"min":
{
"integerValue": "26"
},
"max":
{
"integerValue": "75"
},
"replacementValue":
{
"stringValue": "Medium"
}
},
{
"min":
{
"integerValue": "76"
},
"max":
{
"integerValue": "100"
},
"replacementValue":
{
"stringValue": "High"
}
}
]
}
}
}
...
Cenário de agrupamento por classes 2
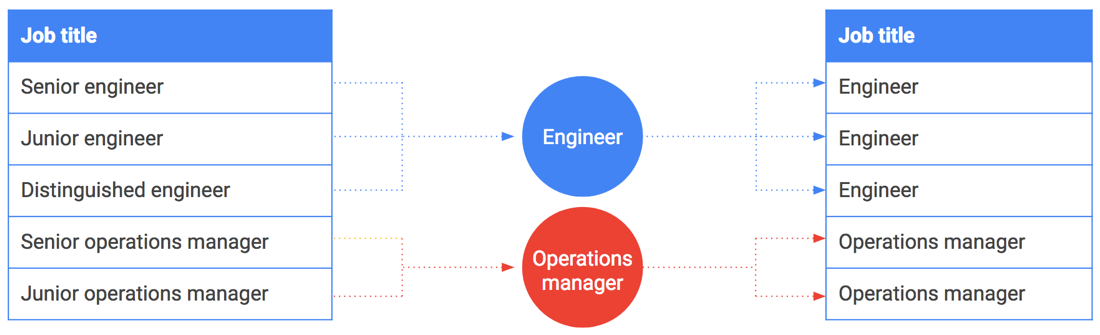
O agrupamento por classes também pode ser usado em strings ou valores enumerados. Suponha que você queira compartilhar dados salariais e incluir cargos. No entanto, alguns cargos, como CEO ou engenheiro renomado, podem ser vinculados a uma pessoa ou a um pequeno grupo de pessoas. Tais cargos são facilmente ligados aos funcionários que os detêm.
O agrupamento por classes pode ajudar aqui também. Em vez de incluir cargos exatos, generalize e agrupe-os por classes. Por exemplo, "engenheiro sênior", "engenheiro júnior" e "engenheiro renomado" tornam-se generalizados e agrupados por classes em simplesmente "engenheiro". A tabela a seguir ilustra esse agrupamento por classes de cargos específicos em famílias de cargos.
Outros cenários
Nestes exemplos, aplicamos a transformação a dados estruturados. O agrupamento por classes também pode ser usado em exemplos não estruturados, desde que o valor possa ser classificado com um infoType predefinido ou personalizado. Veja a seguir alguns cenários de exemplo:
- Classifique datas e agrupe-as por classes em intervalos de ano.
- Classifique nomes e agrupe-os por classes em grupos com base na primeira letra (A-M, N-Z).
Recursos
Para saber mais sobre generalização e agrupamento por classes, consulte Como desidentificar dados confidenciais no conteúdo de texto.
Sobre a documentação da API, consulte:
- Método
projects.content.deidentify - Transformação
BucketingConfig: valores de buckets com base em faixas personalizadas. - Transformação
FixedSizeBucketingConfig: valores de buckets com base em faixas de tamanho fixo.

