This document describes the options for establishing secure and efficient network connectivity between your on-premises networks and your SAP solutions that are running on Google Cloud and managed under the RISE with SAP program.
Establishing this connection is essential for direct data transfer, which avoids routing through on-premises locations and the public internet, and enables seamless communication among your SAP systems, end users, and applications running on Google Cloud. Google Cloud and SAP jointly support several options for connecting your on-premises networks to your RISE with SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition solutions.
This document is meant for cloud architects, network engineers, and developers who help you manage your SAP solutions.
Connect to SAP RISE from your Google Cloud project
To connect your Google Cloud project to the SAP RISE-managed Google Cloud project, review the following:
High-level procedure
Connecting your Google Cloud project to the SAP RISE-managed Google Cloud project involves the following high-level steps:
Identify your Google Cloud VPC network.
Determine the VPC network within your Google Cloud project that needs connectivity to the SAP RISE-managed Google Cloud project. The Google Cloud project that you're determining is assumed to be the connection point to your on-premises systems and users.
Coordinate with SAP and identify the SAP RISE-managed VPC network.
Engage with your SAP representative or the SAP Enterprise Cloud Service (ECS) team to obtain the necessary details about the SAP-managed Google Cloud VPC network hosting your RISE with SAP solution. This includes the VPC network name, project ID of the Google Cloud project, relevant resource identifiers, and the CIDR range that you are to use.
Initiate VPC Network Peering.
By using the details provided by SAP, you typically initiate a VPC Network Peering connection from your Google Cloud project, targeting the VPC network in the SAP RISE-managed Google Cloud project.
Confirm SAP's approval for the network peering request and network configuration.
The SAP RISE team that manages its side of the network, must approve your VPC Network Peering connection request. SAP also must configure its side of the network to establish the peering link back to the VPC network in your Google Cloud project.
Configure routing and security.
Once network peering is established, you configure routing to let traffic flow between your VPC network and the SAP RISE-managed VPC network. To secure this connection, Google Cloud firewall rules or policies can be used on both sides to permit communication only on necessary ports and protocols for SAP systems. For example, those for SAP NetWeaver, SAP HANA, HTTPS, RFC, or JDBC/ODBC.
Use a transit VPC
To connect your Google Cloud project to the SAP RISE-managed Google Cloud project, we recommend that you use a transit VPC architecture, which enables centralized network management.
For information about transit VPC, see Transit network with multiple peerings.
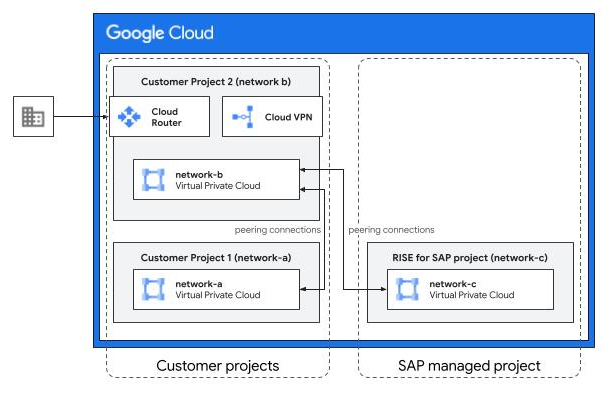
As shown in the preceding example diagram, using a transit VPC architecture can include the following components:
- Google Cloud projects:
- Customer project 1: A Google Cloud project managed by you. This includes Network A, a VPC network.
- Customer project 2: An intermediary Google Cloud project managed by you, and used by your on-premises users to connect to your SAP systems. This includes Network B, a VPC network.
- RISE with SAP project: A Google Cloud project managed by SAP under the RISE with SAP program. This includes Network C, a VPC network.
- Network connections, provided they are allowed by appropriate firewall rules:
- Compute instances in the customer-managed Network A can connect with the instances in the customer-managed Network B and on-premises systems.
- Compute instances in the customer-managed Network B can connect with the instances in the customer-managed Network A, the SAP-managed Network C, and on-premises systems.
- Compute instances in the SAP-managed Network C can connect with the instances in the customer-managed Network B and on-premises systems.
- Compute instances in the customer-managed Network A cannot connect with the instances in the SAP-managed Network C because VPC Network Peering isn't transitive. To allow instances in Network A to connect with instances in Network C, you also need VPC Network Peering between the corresponding Google Cloud projects.
Benefits of using a transit VPC
Using a transit VPC architecture lets you do the following:
- Use existing Dedicated Interconnect or Partner Interconnect networks that connect your on-premises network to Google Cloud.
- Share existing bandwidth already provisioned for your managed VPC networks with one or more SAP-managed VPC networks.
- Make sure that firewall rules are managed according to your organization's policies.
- Deploy third-party firewall products, such as those from Palo Alto Networks Inc., in the transit VPC to be used for all cross-VPC network traffic and to on-premises networks.
- Control Internet traffic in the transit VPC network instead of controlling it in the SAP-managed VPC network.
Alternatives to using a transit VPC
As an alternative to using a transit VPC architecture, you can use one of the following options:
- For more complex or additional security requirements, use a Cloud VPN connection . For more information, see Cloud VPN overview.
- If you need to allow connectivity from multiple Google Cloud projects to the SAP-managed Google Cloud project, then consider the hub-and-spoke architecture. For more information, see Hub-and-spoke network architecture.
Connect to SAP RISE from your on-premises networks
To connect your on-premises networks with your SAP solutions running on the SAP-managed Google Cloud project, you can use one of the following options:
| Connectivity option | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud VPN |
Cloud VPN provides network connectivity between your on-premises network and Google Cloud. It is a lower-cost solution suitable for lower bandwidth needs, a secondary access path, or experimentation. Cloud Router is used with Cloud VPN for dynamic routing. For more information, see Connect with site-to-site VPN. |
| Cloud Interconnect |
Cloud Interconnect offers enterprise-grade connections with higher throughput. It includes the following options:
For connecting to VPC networks, Google recommends that you use Cloud Interconnect instead of Direct Peering, Carrier Peering, or Verified Peering Provider. When you use Cloud Interconnect, traffic flows directly between networks and not through the public internet. This isn't the case when you use Partner Interconnect and don't add IPsec encryption for third-party providers to satisfy data security or compliance requirements. Cloud Router is used with Cloud Interconnect for dynamic routing. For more information, see Connect with Dedicated Interconnect. |
Connect with site-to-site VPN
For connecting your on-premises network to the Google Cloud project where your SAP-managed solution is located, one main method is using site-to-site VPN through Cloud VPN.
For enterprise-grade connections, Google Cloud recommends using HA VPN (High-Availability Cloud VPN) over Classic VPN, as certain dynamic routing functionality in Classic VPN is deprecated.
The technical components and their configuration involved in establishing this site-to-site VPN connection are as follows:
Choose the VPN type: Select HA VPN for a high-availability solution that provides an IPsec VPN connection.
Depending on the topology and configuration, HA VPN can offer 99.99% or 99.9% service availability.
Configure the Google Cloud resources:
Create an HA VPN gateway in your Google Cloud project.
Google Cloud automatically assigns two external IP addresses to this gateway, one for each of its interfaces, to support high availability. Each HA VPN gateway interface supports multiple tunnels.
Configure an external VPN gateway resource in Google Cloud.
This resource provides information to Google Cloud about your peer VPN gateway, which is your VPN device located on your on-premises network.
Use a Cloud Router, which is used in conjunction with Cloud VPN gateways. Cloud Router provides dynamic routing by using Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
Configure the on-premises resources:
Configure your on-premises VPN device. This is the "peer VPN gateway" represented by the "external VPN gateway" resource in Google Cloud.
The VPN device establishes IPsec tunnels to the public IP addresses of the HA VPN gateway.
Configure BGP on your on-premises router to peer with the Cloud Router in Google Cloud. This facilitates the exchange of route information.
Establish dynamic routing: Cloud Router learns routes to your on-premises network by using BGP peering and applies the learnt routes as custom dynamic routes in your VPC network. Conversely, your on-premises network uses BGP from the Cloud Router to learn routes to the Google Cloud VPC network.
Using Cloud Router with BGP provides dynamic route exchange, which simplifies network management compared to static routing.
This configuration results in a secure and reliable connection through an encrypted IPsec tunnel, enabling direct data transfer and communication between your on-premises environment and the Google Cloud project managed by SAP.
Connect with Cloud Interconnect
Cloud Interconnect connections provide direct access to your Google Cloud VPC network resources that have only internal IP addresses.
Cloud Interconnect offers two main options for connecting your on-premises network: Dedicated Interconnect and Partner Interconnect.
Dedicated Interconnect: This service lets you establish a direct physical connection between your network in a supported colocation facility and Google's edge network, providing dedicated 10-Gbps or 100-Gbps circuits with flexible VLAN attachment capacities. Traffic flows directly between your network and Google's network, bypassing the public internet.
For more information about Dedicated Interconnect, see Dedicated Interconnect overview.
Partner Interconnect: If you can't directly connect to Google's network, then use Partner Interconnect. This service lets you connect through a supported service provider who has established connectivity to Google.
Partner Interconnect offers flexible capacities starting at 50 Mbps, and your traffic flows between your network and Google's network through the service provider, not the public internet. For more information, see Partner Interconnect overview.
Regardless of whether you choose Dedicated Interconnect or Partner Interconnect, the Google Cloud side of the connectivity uses a Cloud Router. The Cloud Router provides dynamic routing between your on-premises network and your VPC network by using BGP. You configure your on-premises routers to peer with the Cloud Router, enabling automatic exchange of route information. The Cloud Router learns routes to your on-premises network by using BGP and applies these as custom dynamic routes in your Google Cloud VPC network. This dynamic routing simplifies network management compared to static routing.
While the physical connection enabled by Cloud Interconnect itself provides privacy, you can optionally deploy HA VPN over Cloud Interconnect to add IPsec encryption for traffic between your network and Google's network.
When you use Cloud Interconnect for Google-defined topologies, Google offers an end-to-end SLA for connectivity between your Google Cloud VPC network and on-premises network.
