Bereiten Sie das Upgrade Ihrer vorherigen Installation von Knative Serving vor und migrieren Sie Ihre Arbeitslasten. Richten Sie dazu Ihre Befehlszeilenumgebung ein, erstellen Sie Umgebungsvariablen und laden Sie das Migrationsskript herunter.
Hinweise
Sie müssen zuerst prüfen, ob die Anforderungen erfüllt sind, bevor Sie ein Upgrade ausführen.
Standardmäßig enthält Cloud Shell die neuesten Versionen der
gcloud- undkubectl-Befehle. Wenn Sie die Befehlszeilenumgebung Ihres lokalen Computers verwenden, müssen Sie die folgenden Mindestanforderungen erfüllen:gcloud-Version 1.16.13 oder höherkubectl-Clientversion 1.21 oder höher
Die Vorbereitungsschritte auf dieser Seite sind für den gesamten Upgrade- und Migrationsprozess erforderlich.
Wichtig: Alle Befehle, die während des Prozesses verwendet werden, basieren auf den unten festgelegten Umgebungsvariablen. Wenn Sie beispielsweise Cloud Shell schließen oder das Zeitlimit Ihrer Sitzung überschritten wird, müssen Sie dafür sorgen, dass die erforderlichen Umgebungsvariablen zurückgesetzt werden.
Richten Sie Ihre Umgebung ein.
Öffnen Sie Cloud Shell in der Google Cloud Console, um Cloud Shell zu verwenden:
Wichtig: Für Cloud Shell gelten Nutzungslimits und es kann eine Zeitüberschreitung auftreten. Wenn Ihre Sitzung das Zeitlimit überschreitet, müssen Sie dafür sorgen, dass die erforderlichen Umgebungsvariablen zurückgesetzt werden.
Erstellen Sie die folgenden erforderlichen Umgebungsvariablen:
Legen Sie Variablen für Ihr Google Cloud -Projekt und die Clusterdetails fest:
export PROJECT_ID=PROJECT_ID export CLUSTER_NAME=CLUSTER_NAME export CLUSTER_LOCATION=CLUSTER_LOCATIONErsetzen Sie Folgendes:
- PROJECT_ID durch die ID Ihres Google Cloud-Projekts.
- CLUSTER_NAME durch die ID Ihres Clusters oder die voll qualifizierte ID für den Cluster.
- CLUSTER_LOCATION durch die Region oder Zone, in der sich der Cluster befindet.
Abhängig von Ihrer Konfiguration müssen Sie das Ingress-Gateway identifizieren, das den Traffic in Ihrem Cluster verarbeitet. Es ist wichtig zu ermitteln, welche Version von Istio tatsächlich konfiguriert ist und Traffic bereitstellt.
Wenn Sie die gebündelte Version von Istio verwenden, prüfen Sie, ob der Name des Ingress-Dienstes im Namespace
gke-systemso lautet:istio-ingress.kubectl get svc istio-ingress -n gke-systemErgebnis: Die Details Ihrer Konfiguration werden zurückgegeben.
Wenn Sie das Istio-Add-on installiert haben, müssen Sie ermitteln, welches Ingress-Gateway konfiguriert ist und den Traffic aktiv verarbeitet, indem Sie die IP-Adressen der Dienste abrufen und ermitteln, welche davon für Ihre Domain konfiguriert ist.
Rufen Sie für jeden Ingress-Dienst die
EXTERNAL-IP-Adresse ab:Führen Sie die folgenden Befehle aus, um die Konfigurationsdetails der Ingress-Dienste der gebündelten Version von Istio (
istio-ingress) und des Istio Add-ons (istio-ingressgateway) abzurufen:kubectl get svc istio-ingress -n gke-system kubectl get svc istio-ingressgateway -n istio-systemBeispielausgabe:
Notieren Sie sich für jeden Dienst den Wert von
EXTERNAL-IP.NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE istio-ingress LoadBalancer 11.11.1.111 12.345.678.910 15020:31265/TCP,80:30059/TCP,443:32004/TCP 8d NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 22.22.2.222 10.987.654.321 15021:32747/TCP,80:30695/TCP,443:32695/TCP,15012:32369/TCP,15443:30909/TCP 88dErmitteln Sie, über den DNS-Eintrag Ihrer benutzerdefinierten Domain, welche externe IP-Adresse für die Verarbeitung von Traffic konfiguriert ist:
Rufen Sie die Seite „Knative Serving-Domainzuordnungen“ auf:
Klicken Sie auf das Dreipunkt-Menü rechts neben Ihrem Dienst und dann auf DNS-EINTRÄGE, um alle DNS-Einträge aufzurufen:
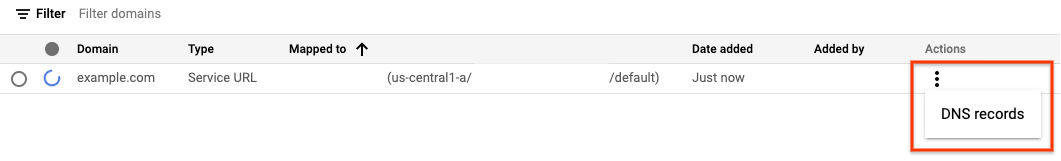
Im obigen Beispiel wird das Istio-Add-on-Ingress-Gateway verwendet und Traffic bereitgestellt, wenn die DNS-Eintragskonfiguration auf die IP-Adresse
10.987.654.321desistio-ingressgateway-Dienstes festgelegt ist.
Legen Sie Variablen für den Namen und den Namespace des Ingress-Dienstes fest, der Traffic für Ihren Cluster bereitstellt:
export INGRESS_NAME=INGRESS_NAME export INGRESS_NAMESPACE=INGRESS_NAMESPACEErsetzen Sie Folgendes:
INGRESS_NAME durch den Namen des Dienstes für eingehenden Traffic, den Sie im vorherigen Schritt identifiziert haben.
INGRESS_NAMESPACE durch den Namespace des Ingress-Dienstes, den Sie im vorherigen Schritt identifiziert haben.
Google Cloud CLI konfigurieren:
gcloud config set project ${PROJECT_ID} gcloud container clusters get-credentials ${CLUSTER_NAME} --region ${CLUSTER_LOCATION}Für private Cluster:
Wenn Sie bereits Zugriff auf Ihren privaten Cluster über den Client haben, auf dem Sie das Migrationsskript ausführen, können Sie mit dem nächsten Schritt fortfahren.
Wenn für Ihren privaten Cluster
master-authorized-networkaktiviert ist, können Sie den Zugriff über den Client aktivieren, auf dem Sie das Migrationsskript ausführen. Fügen Sie dazu die IP-Adresse des Clients in die Zulassungslistemaster-authorized-networksein:gcloud container clusters update ${CLUSTER_NAME} \ --region=${CLUSTER_LOCATION} \ --enable-master-authorized-networks \ --master-authorized-networks $(curl ifconfig.me)/32
Laden Sie das Migrationsskript für Knative Serving herunter:
TMP_DIR=$(mktemp -d) gcloud storage cp gs://crfa-to-hub-upgrade/migration-addon.sh $TMP_DIR cd $TMP_DIR chmod +x ./migration-addon.shFühren Sie den folgenden Befehl aus, um die Skalierung auf null zu deaktivieren. Andernfalls schlägt die Skalierung fehl und führt zu Fehlern, wenn der Master-Knoten aktualisiert wird:
kubectl patch cm config-autoscaler -n knative-serving -p '{"data":{"enable-scale-to-zero": "false"}}'Beachten Sie, dass der letzte Schritt in diesem Upgrade- und Migrationsprozess darin besteht, die Skalierung auf null wieder zu aktivieren.

