本主题介绍了有关将密钥作为新密钥版本导入到 Cloud Key Management Service 的概念信息。如需了解分步说明,请参阅导入密钥版本。
简介
您可能正在使用在本地或外部密钥管理系统中创建的现有加密密钥。如果您将应用迁移到Google Cloud ,或者向现有Google Cloud 应用添加加密支持,则可以将相关密钥导入 Cloud KMS。
- 您可以导入到 Cloud KMS 中的 Cloud HSM 密钥或软件密钥。
- 密钥材料会进行封装以便在传输过程中受到保护。您可以使用 Google Cloud CLI 自动封装密钥,也可以手动封装密钥。
- Google Cloud 只能在导入作业的范围内访问封装密钥。 对于 Cloud HSM 密钥,封装密钥永不位于 Cloud HSM 之外。
本主题详细介绍有关导入密钥的限制和要求,并简要介绍了密钥导入的工作原理。
限制和要求
查看这些部分以确认您的密钥可以导入到 Cloud KMS 中。
支持的密钥格式
- 用于加密的对称密钥: 导入的对称密钥必须为 16 个字节(仅适用于原始对称加密)或 32 个字节的二进制数据,并且不得经过编码。 如果您的密钥是十六进制编码或 base64 编码的密钥,则必须先对其进行解码,然后再尝试导入。
- 用于签名的对称密钥(MAC 密钥):导入的 HMAC 签名密钥的长度必须等于所用加密哈希函数的输出长度(例如,HMAC-SHA256 密钥的长度必须为 32 个字节),并且不得进行编码。如果您的密钥是十六进制编码或 base64 编码的密钥,则必须先对其进行解码,然后再尝试导入。
- 用于加密或签名的非对称密钥:导入的非对称密钥必须采用 PKCS #8 格式,且必须经过 DER 编码。PCKS #8 格式在 RFC 5208 中定义。DER 编码定义在 International Telecommunications Union X.680 中。非对称密钥必须使用 Cloud KMS 支持的其中一个长度和算法组合。
密钥一经创建,密钥的某些方面(例如密钥的长度)便无法更改。在这些情况下,密钥无法导入到 Cloud KMS 中。
如需验证密钥并重新设置密钥的格式以进行导入,请参阅设置密钥的格式以进行导入。
支持的保护级别
通过将密钥的保护级别设置为SOFTWARE 或 HSM,您可以将密钥导入为 Cloud KMS 密钥或 Cloud HSM 密钥。Cloud HSM 密钥会产生额外的费用。
您无法导入到 Cloud External Key Manager 密钥中。
支持的封装密钥大小
创建导入作业时,您可以通过设置导入作业的导入方法来控制保护向 Google Cloud 传输的密钥的封装密钥的大小。封装密钥的默认大小为 3072。如果您有特定要求,可以将导入作业配置为使用 4096 位密钥。
密钥导入的工作原理
本部分介绍导入密钥时发生的情况。如果您使用自动封装或手动封装密钥,流程的某些部分会有所不同。建议使用自动封装。如需了解具体说明,请参阅导入密钥版本。有关在导入前手动封装密钥的具体说明,请参阅在 Linux 上使用 OpenSSL 封装密钥。
下图展示了使用自动密钥封装的密钥导入过程。本部分介绍图中显示的各个阶段。
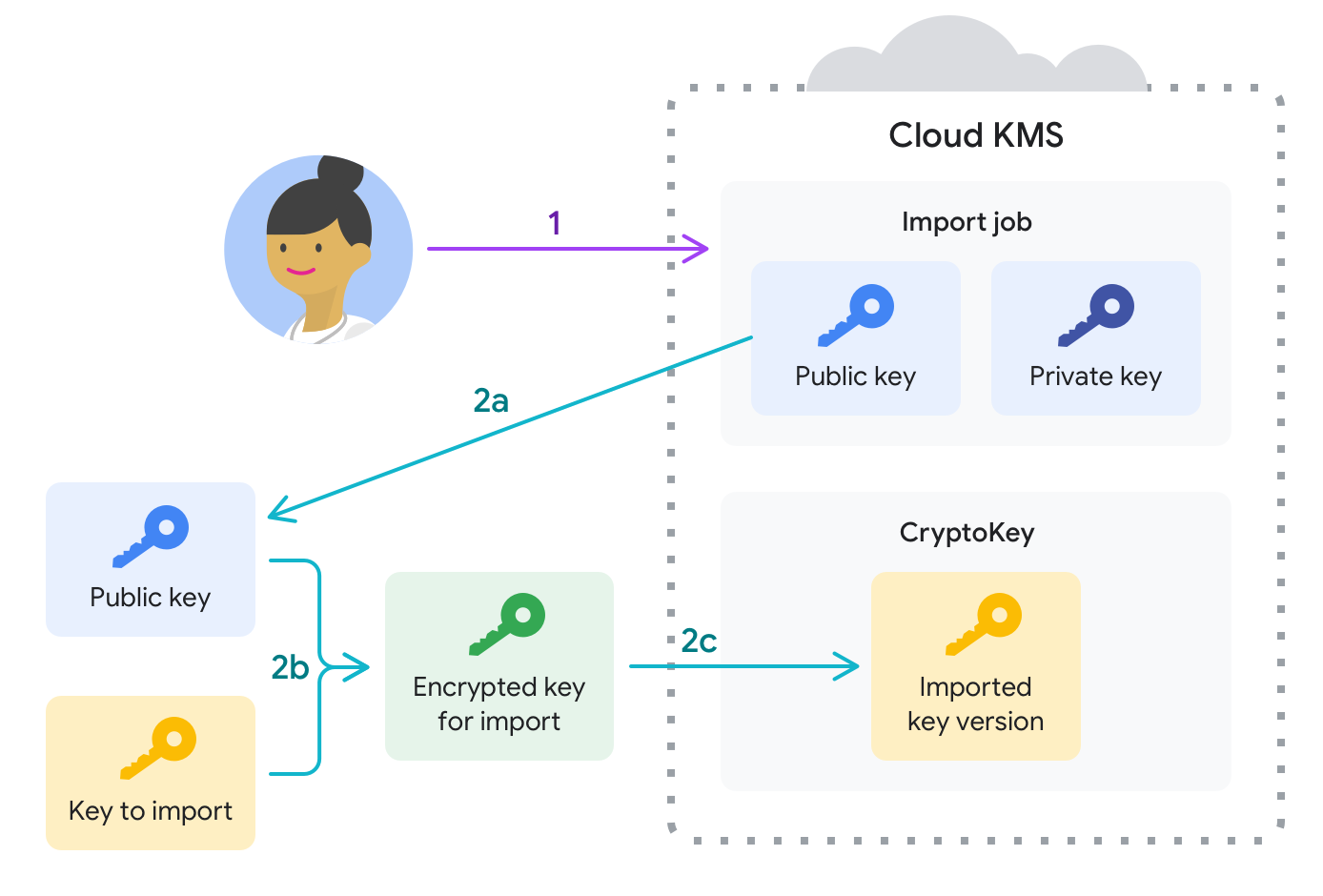
准备导入密钥。
首先,创建一个目标密钥环和密钥,它们将最终包含导入作业和导入的密钥材料。此时,目标密钥不包含任何密钥版本。
接下来创建导入作业。导入作业定义导入的密钥材料的目标密钥环和密钥。导入作业还定义了导入方法,这是用于创建封装密钥以在导入请求期间保护密钥材料的算法。
- 公钥用于封装要在客户端上导入的密钥。
- 私钥存储在 Google Cloud 中,用于在密钥到达 Google Cloud 项目后对其进行解封装。
这种分离可防止 Google 在导入作业范围之外解封您的密钥材料。
在密钥传输到 Google 之前,必须先对其进行加密封装。大多数用户都可以使用 gcloud CLI 自动封装、传输和导入密钥,如下一步所述。如果您满足手动封装密钥的合规性或监管要求,现在就可以这么做。如需在本地系统中手动封装密钥,请执行以下操作:
- 配置 OpenSSL。
- 下载与导入作业关联的封装密钥(每个导入作业一次)。
- 设置多个环境变量并封装密钥(每个密钥一次)。
在最多三天的时间内,您可以在导入作业过期之前发出导入请求来导入一个或多个密钥。在导入请求期间:
- 如果未手动封装密钥,则 Google Cloud CLI 会将导入作业的公钥从 Google Cloud 下载到本地系统,然后使用该公钥以及与客户端关联的私钥来封装本地密钥材料。
- 封装的密钥材料将传输到 Google Cloud项目。
- 系统会使用导入作业的私钥解封装密钥材料,并将其作为目标密钥环上的目标密钥的新版本插入。这是一个原子操作。
- 对于对称密钥,将导入的密钥版本设置为主密钥版本。
导入请求成功完成后,您可以使用导入的密钥版本来保护 Google Cloud中的数据。

