Objetivos
Use o Dataproc Hub para criar um ambiente de notebook do JupyterLab de usuário único em execução em um cluster do Dataproc.
Crie um notebook e execute um job do Spark no cluster do Dataproc.
Exclua o cluster e preserve o notebook no Cloud Storage.
Antes de começar
- O administrador precisa conceder a você a permissão
notebooks.instances.use(consulte Definir papéis Identity and Access Management (IAM)).
Criar um cluster do JupyterLab do Dataproc no Dataproc Hub
Selecione a guia Notebooks gerenciados pelo usuário na página Dataproc→Workbench no console Google Cloud .
Clique em Abrir JupyterLab na linha que lista a instância do Dataproc Hub criada pelo administrador.
- Se você não tiver acesso ao console Google Cloud , insira o URL da instância do Dataproc Hub que um administrador compartilhou com você no navegador da Web.
Na página Jupyterhub→Opções do Dataproc, selecione uma configuração de cluster e uma zona. Se estiver ativado, especifique as personalizações e clique em Criar.
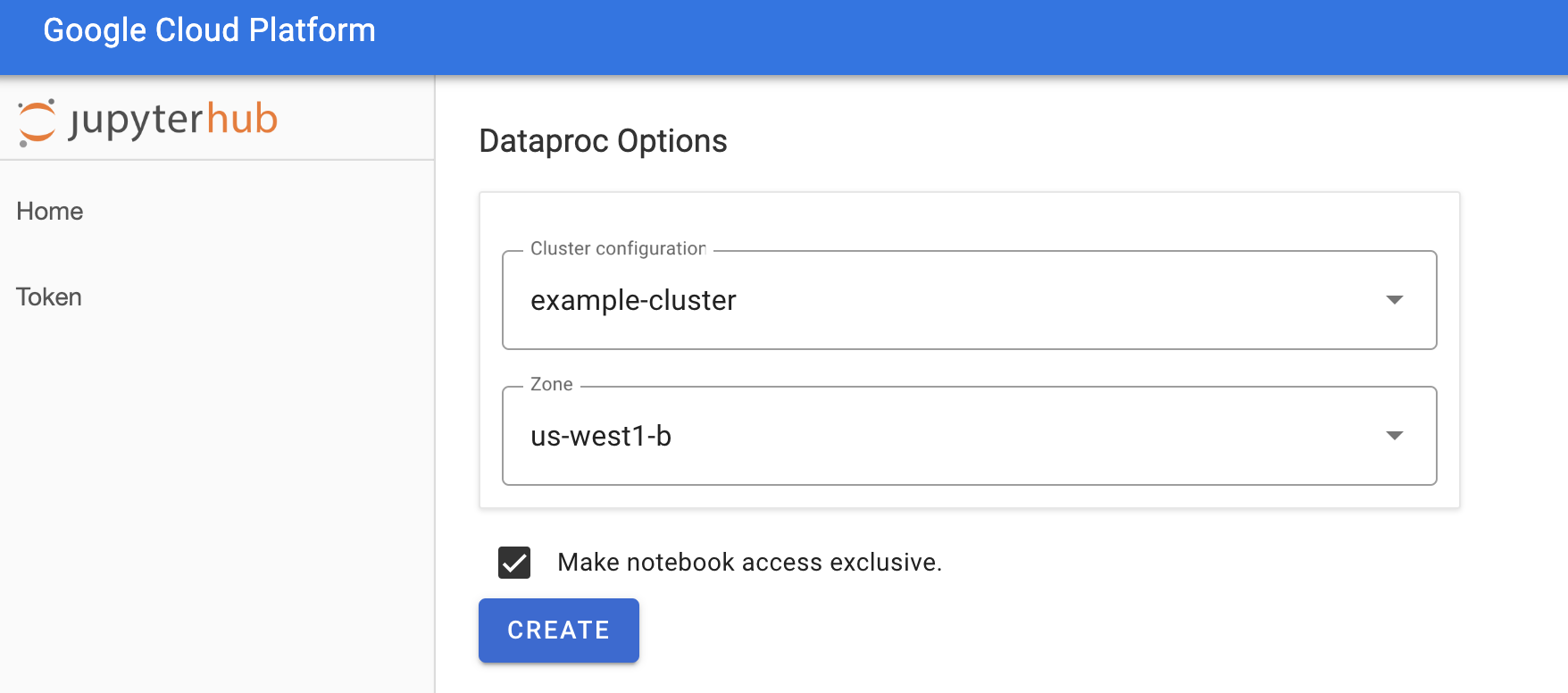
Depois que o cluster do Dataproc for criado, você será redirecionado para a interface do JupyterLab em execução no cluster.
Criar um notebook e executar um job do Spark
No painel esquerdo da interface do JupyterLab, clique em
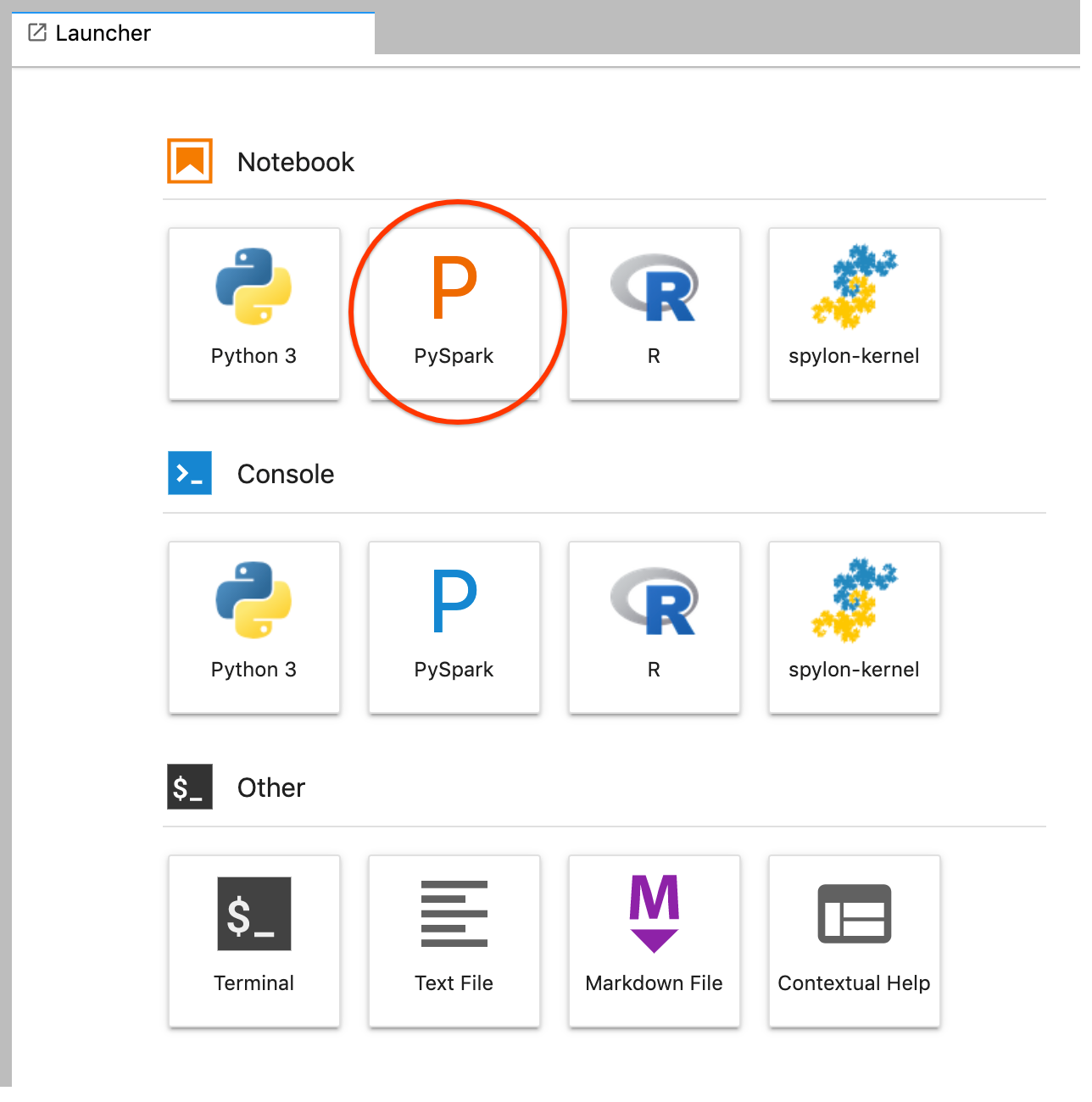
GCS(Cloud Storage).Crie um notebook PySpark no iniciador do JupyterLab.
O kernel do PySpark inicializa um SparkContext (usando a variável
sc). Você pode examinar o SparkContext e executar um job do Spark no notebook.rdd = (sc.parallelize(['lorem', 'ipsum', 'dolor', 'sit', 'amet', 'lorem']) .map(lambda word: (word, 1)) .reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b)) print(rdd.collect())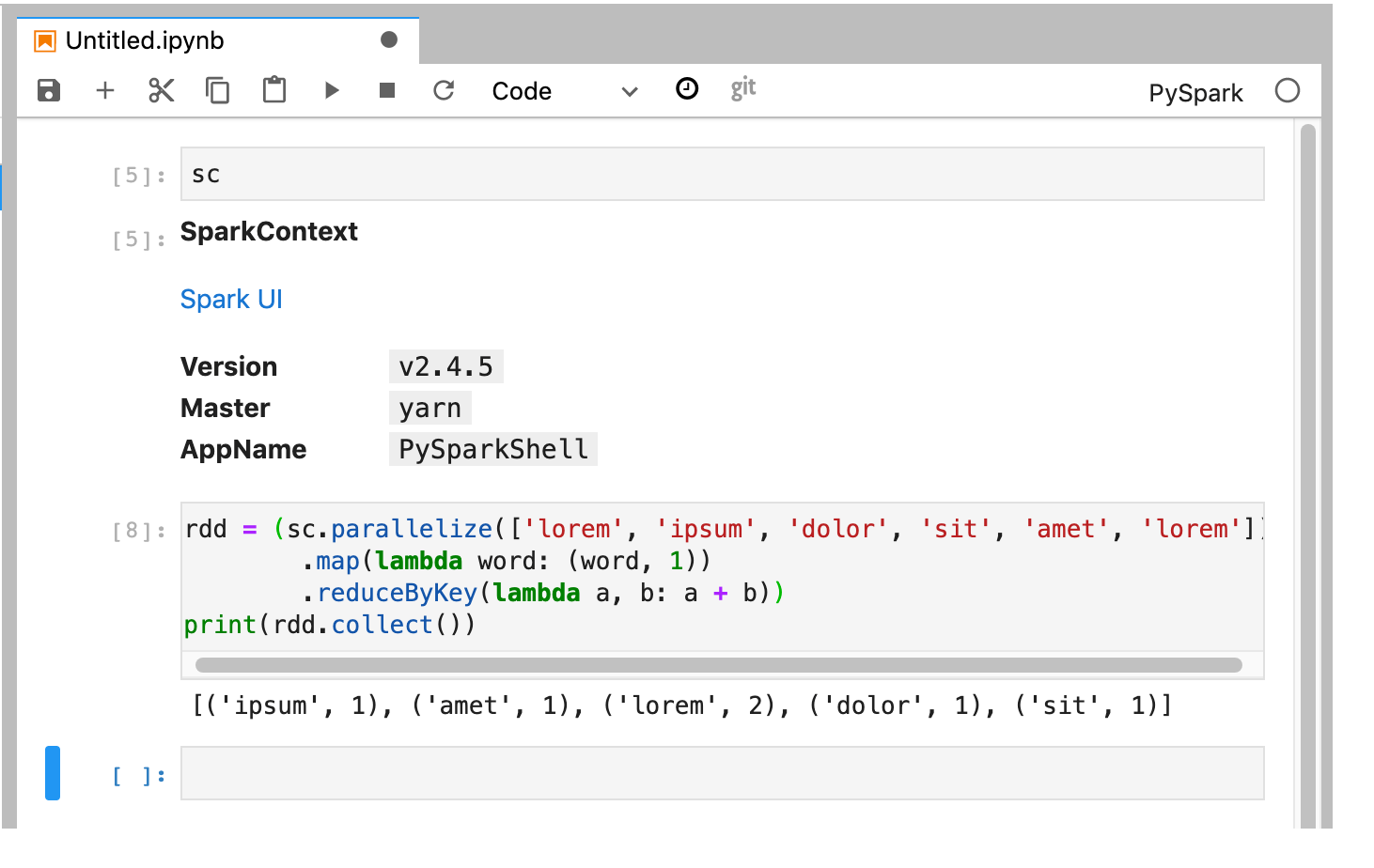
Nomeie e salve o notebook. O notebook é salvo e permanece no Cloud Storage depois que o cluster do Dataproc for excluído.
Encerrar o cluster do Dataproc
Na interface do JupyterLab, selecione Arquivo→Painel de controle do hub para abrir a página Jupyterhub.
Clique em Parar Meu cluster para encerrar (excluir) o servidor do JupyterLab, que exclui o cluster do Dataproc.
A seguir
- Conheça os notebooks Spark e Jupyter no Dataproc no GitHub.

