Linux 系统容器简介
借助 Migrate to Containers CLI,您可以将基于 Linux 的应用迁移到容器化环境。它使用预构建的 Linux 系统容器充当现代化应用所需服务的引导加载程序。借助 Migrate to Containers for Linux 应用,您可以对各种无状态应用进行现代化改造,以便在 Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)、Cloud Run 和 GKE 集群上运行。
如需了解详情,请参阅 Migrate to Containers CLI 架构。
本文档详细介绍了 Migrate to Containers Linux 系统容器,运行使用 Migrate to Containers 迁移的应用的解决方案中包含这些容器。
使用 Linux 系统容器进行迁移
Migrate to Containers 会发现源应用文件和进程。然后,它会生成包含 Dockerfile、Kubernetes 清单和 Skaffold 配置的工件。
Linux 系统容器的主要功能是启动最初在源虚拟机 (VM) 实例中运行的服务,包括相关的操作系统和应用服务。
Dockerfile 用于为迁移后的虚拟机构建映像。Linux 系统容器 Dockerfile 通常如下所示:
# Please refer to the documentation:
# https://cloud.google.com/migrate/anthos/docs/dockerfile-reference
FROM us-docker.pkg.dev/migrate-modernize-public/modernize-plugins-prod/service-manager-runtime:1.0.0 as service-manager-runtime
FROM scratch
# Tar containing data captured from the source VM
ADD vmFiles.tar.gz /
COPY --from=service-manager-runtime / /
ADD blocklist.yaml /.m4a/blocklist.yaml
ADD logs.yaml /code/config/logs/logsArtifact.yaml
ADD services-config.yaml /.m4a/
ADD tempfiles.yaml /.m4a/
# If you want to update parts of the image, add your commands here.
# For example:
# RUN apt-get update
# RUN apt-get install -y \
# package1=version \
# package2=version \
# package3=version
# RUN yum update
# RUN wget http://github.com
ENTRYPOINT ["/ko-app/service-manager-runtime", "start", "-c", "/.m4a/"]
执行迁移时,以下 Dockerfile 语句将原始来源中的虚拟机数据复制或添加到 Docker 映像:
以下语句将从源虚拟机捕获的数据所在的 tar 文件添加到 Docker 映像:
ADD vmFiles.tar.gz /此 tar 由 Migrate to Containers 创建。它包含源虚拟机的根文件系统,其中包含迁移计划的过滤条件中提供的所有内容,以及过滤掉的数据迁移计划中提供的任何文件夹。
以下语句将 Docker 代码库中的 Migrate to Containers 运行时导入 Docker 映像:
FROM us-docker.pkg.dev/migrate-modernize-public/modernize-plugins-prod/service-manager-runtime:1.0.0 as service-manager-runtime以下语句随后将 Migrate to Containers 运行时复制到 Docker 映像:
COPY --from=service-manager-runtime / /
点击即可查看有关 Migrate to Containers 运行时文件的详细信息
/ko-app/service-manager-runtime 是主要的 Migrate to Containers 运行时文件。这是一个专为容器打造的初始化系统。它执行以下操作:
- 读取
/.m4a/services-config.yaml文件,并根据指定的运行方法(例如守护进程化、非守护进程化、等待完成)按顺序运行指定的二进制文件。 - 收集
/code/config/logs/logsArtifact.yaml文件中指定的日志,并将其输出到容器的stdout。对于 GKE 和 GKE 集群,还可以确保将日志发送到 Cloud Logging。
维护迁移的工作负载
您可以使用迁移后的工件为您的应用创建新的流水线。您可能会为不同的应用使用不同的流水线。您可以保留生成了基于原始虚拟机的应用的现有持续集成和部署流水线,并添加将生成的可执行文件转换为 Linux 系统容器的相关步骤。
下图展示了使用 Migrate to Containers 的示例流水线:
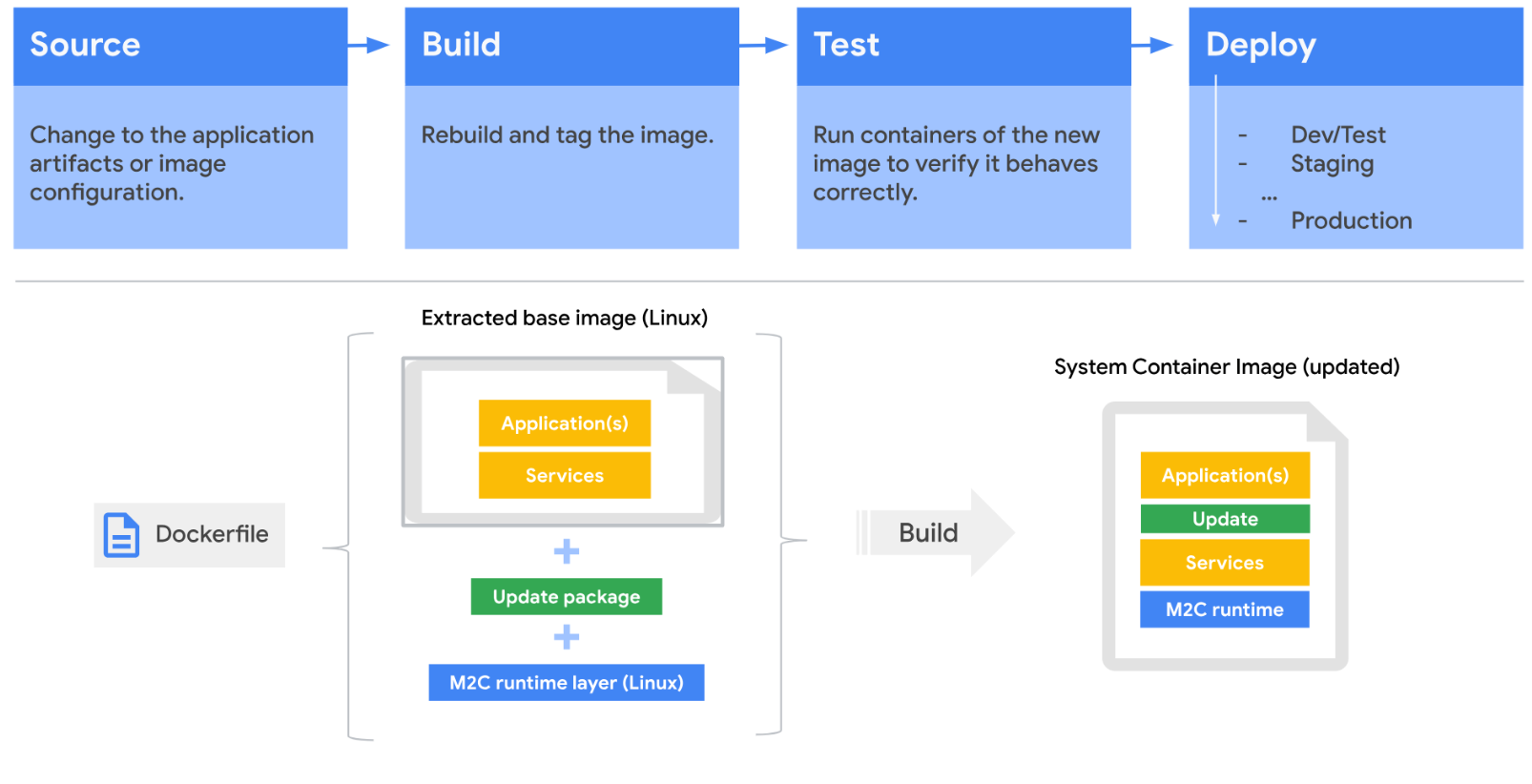
下图显示了现有应用的更改过程。
对源代码或新操作系统路径的更改将被推送到现有 Git 代码库。然后会根据现有设置编译源代码,并构建新映像。新映像包含 Migrate to Containers 运行时层。
在测试环境中,开发者运行初步测试,以确认新映像是否按预期工作。测试阶段完成后,将创建一个新的系统容器映像,该映像会推送到开发或测试环境,稍后再发布到生产环境。
