本文档提供了自动部署自动调节式保护生成的建议规则的配置步骤。如需启用自动规则部署,您必须创建具有以下值的占位符规则:
- 匹配表达式:
evaluateAdaptiveProtectionAutoDeploy() - 操作:任何
- 优先级:任何。对于优先级高的合法流量,我们建议您将显式允许规则设置为具有比其他规则更高的优先级。
如果您在外部应用负载均衡器前端使用上游代理(例如第三方 CDN),则可以将占位符规则配置为根据一个或多个指定标头中的原始客户端 IP 地址来匹配请求。如需使用此预览版功能,请在 advancedOptionsConfig 字段中配置 userIpRequestHeaders[] 选项。如需了解详情,请参阅 ComputeSecurityPolicy 资源参考文档。
占位符规则示例
以下命令是名为 POLICY_NAME 的安全政策的示例占位符规则,其中每个规则都具有不同的规则操作。您可以将这些规则添加到现有安全政策,也可以创建新政策。如需详细了解如何创建安全政策,请参阅配置 Cloud Armor 安全政策。
阻止恶意流量
对于 Adaptive Protection 识别为攻击流量的请求,此示例规则的求值结果为 true。Cloud Armor 会对攻击请求应用阻止操作。
gcloud compute security-policies rules create 1000 \
--security-policy POLICY_NAME \
--expression "evaluateAdaptiveProtectionAutoDeploy()" \
--action deny-403
将恶意流量重定向到 reCAPTCHA 验证
此示例规则将自动调节式保护识别为恶意的流量重定向到 reCAPTCHA 验证:
gcloud compute security-policies rules create 1000 \
--security-policy POLICY_NAME \
--expression "evaluateAdaptiveProtectionAutoDeploy()" \
--action redirect \
--redirect-type google-recaptcha
限制恶意流量的速率
此示例将 Cloud Armor 速率限制应用于 Adaptive Protection 识别为恶意的流量:
gcloud compute security-policies rules create 1000 \
--security-policy POLICY_NAME \
--expression "evaluateAdaptiveProtectionAutoDeploy()" \
--action throttle \
--rate-limit-threshold-count 500 \
--rate-limit-threshold-interval-sec 120 \
--conform-action allow \
--exceed-action deny-404 \
--enforce-on-key ip
配置自动调节式保护自动部署参数
您可以通过调整以下参数来配置阈值的自动部署阈值。如果您未设置参数的值,Cloud Armor 会使用默认值。
负载阈值:在所提醒的攻击期间,只有当受攻击的后端服务的负载超出此阈值时,自动调节式保护才会识别新的攻击者。此外,只有当受攻击的后端服务的负载超出此阈值时,系统才会针对提醒自动部署规则。
默认值:
0.8
置信度阈值:系统仅针对置信度分数超过此阈值的潜在攻击的提醒自动部署规则。
- 默认值:
0.5
- 默认值:
受影响的基准阈值:仅当建议的缓解措施对基准流量的预计影响低于此阈值时,系统才会自动部署规则。
impactedBaselineProportion和impactedbaselinePolicyProportion应低于受影响的基准阈值。- 默认值:
0.01(1%)
- 默认值:
设置的到期时间:在此时长之后,Cloud Armor 会停止将自动部署的规则中的操作应用于已识别的攻击者。该规则会继续针对新请求执行。
- 默认值:
7200秒
- 默认值:
您可以使用以下示例命令更新安全政策,以使用非默认的自动部署阈值。将 NAME 替换为您的安全政策的名称,并将其余变量替换为您希望用于政策的值。
gcloud beta compute security-policies update NAME [
--layer7-ddos-defense-auto-deploy-load-threshold LOAD_THRESHOLD
--layer7-ddos-defense-auto-deploy-confidence-threshold CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD
--layer7-ddos-defense-auto-deploy-impacted-baseline-threshold IMPACTED_BASELINE_THRESHOLD
--layer7-ddos-defense-auto-deploy-expiration-sec EXPIRATION_SEC
]
日志记录
通过自动调节式保护自动部署的规则生成的日志包含以下额外字段:
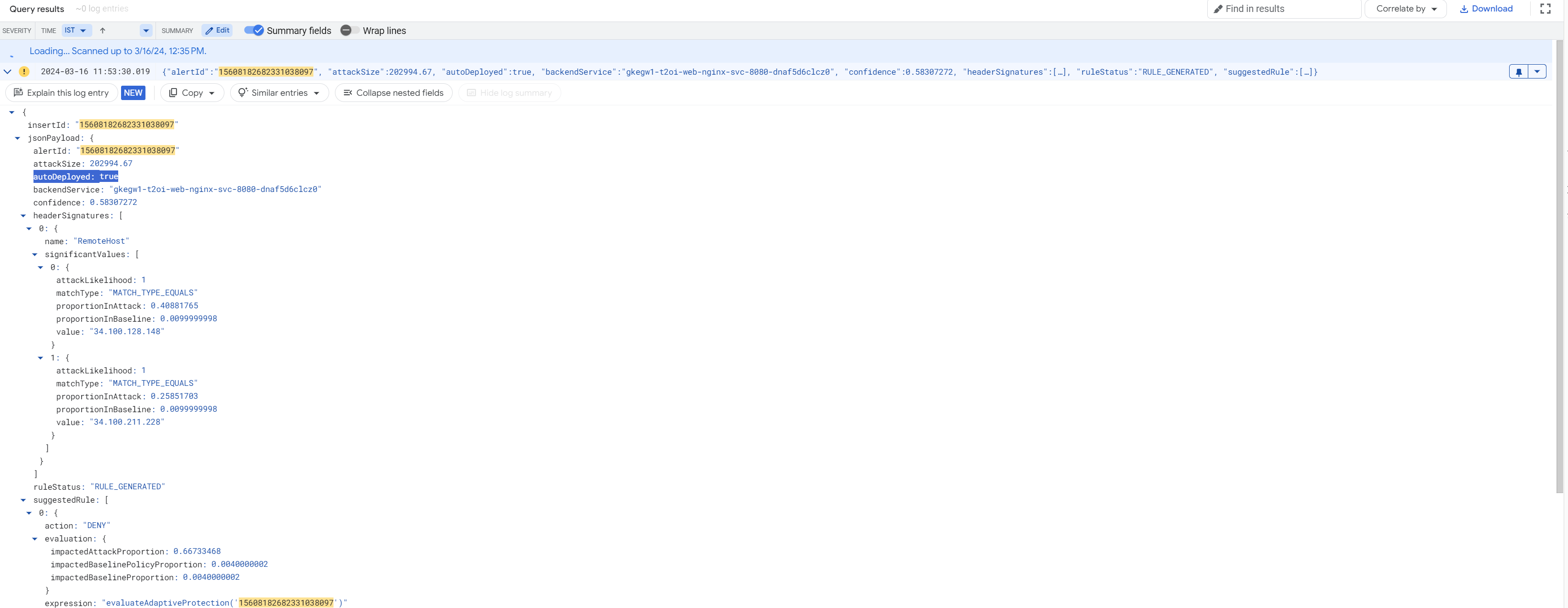
autoDeployed:配置自动规则部署后,自动调节式保护生成的每个提醒日志都包含布尔值字段autoDeployed,用于指示是否触发了自动防御。 当autoDeployed设置为true时,表示evaluateAdaptiveProtectionAutoDeploy()占位符规则已评估出攻击置信度和受影响的基准阈值超出配置的自动部署参数。系统随后开始监控动态负载。一旦负载超过配置的负载阈值,系统便会自动部署规则来缓解攻击。adaptiveProtection.autoDeployAlertId:每当自动调节式保护在自动防御的过程中对请求执行操作时,请求日志都会包含额外的adaptiveProtection.autoDeployAlertId字段,用于记录提醒 ID。此字段会显示在enforcedSecurityPolicy或previewSecurityPolicy下,具体取决于安全政策是否处于预览模式。
如需查看请求日志,请参阅使用请求日志记录。以下屏幕截图显示了包含 autoDeployed 和 adaptiveProtection.autoDeployAlertId 字段的自动调节式保护日志条目示例。
限制
- 自动调节式保护仅适用于附加到通过外部应用负载均衡器公开的后端服务的后端安全政策。自动调节式保护不适用于外部代理网络负载均衡器。
