Symptom
Your client application may experience connection reset, connection refused, or similar errors during the TLS handshake when calling the Apigee endpoint.
Error messages
Postman or Node.js clients may see ECONRESET error messages.
Curl may show Connection reset by peer when making HTTPS calls directly to the Apigee Ingress IP address. For example:
curl https://1.2.3.4/basepath -H "Host: your.apigee.domain" -kv * Connected to 1.2.3.4 (1.2.3.4) port 443 * (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1): * Recv failure: Connection reset by peer * Closing connection
-
Other clients may display different errors. However, the pattern would be the same; the client is unable to establish a connection fully during the TLS handshake.
Possible causes
Apigee Hybrid's Ingress Gateway is Server Name Indication (SNI) enabled by default. This issue can occur if your client is not SNI enabled and there is no wildcard Apigee route configured to enable non-SNI clients. This results in no default TLS server certificate being sent to the client, and an Apigee ingress TCP reset occurs.
Diagnosis
Determine if your client is SNI enabled. If you already know that it's not SNI enabled, proceed to step 4 to validate the Apigee Hybrid configuration.
Review the Apigee Ingress access logs for signs of client requests without the SNI server name, and check if virtual hosts are not configured with a default certificate for non-SNI clients.
- Get a listing of your
apigee-ingressgatewaypods with the following command:kubectl -n apigee get pods -l app=apigee-ingressgateway
Sample output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE apigee-ingressgateway-ext-ingress-myorg-hyb-8f2c412-dvrcp 2/2 Running 0 46h apigee-ingressgateway-ext-ingress-myorg-hyb-8f2c412-wg26k 2/2 Running 0 46h
- Get the logs for an
apigee-ingressgatewaypod.kubectl -n apigee logs APIGEE_INGRESSGATEWAY_POD
apigee-ingressgatewaypod listed in the previous command output. - An access log may look like the following:
{ "request_time": 1, "tls_protocol": null, "upstream_service_time": null, "request_method": null, "request_protocol": null, "upstream_response_time": null, "bytes_sent": 0, "start_time": "2025-05-19T04:46:20.117Z", "bytes_received": 0, "host": null, "upstream_cluster": null, "upstream_address": null, "remote_address": "10.138.0.28:19432", "request_path": null, "request_id": null, "user_agent": null, "status_details": "filter_chain_not_found", "request": "- - -", "status": 0, "x_forwarded_for": null, "apigee_dynamic_data": null, "upstream_response_flags": "NR", "sni_host": null } - Analyzing the preceding log, you can infer the following:
"sni_host": null: The client is not SNI enabled as there is no SNI host name. For ex ample,api-test.mydomain.comis associated with this request."status_details": "filter_chain_not_found": Server certificates are selected based on afilter chainwhich is based on thesni_host. If nosni_hostexists and no default is configured, thefilter chaincannot be found. This means no server certificate is returned, as seen in the example client request."status": 0: There's no status code as the connection was reset.
- Instead of reviewing logs, a more precise way to check if a client is SNI enabled would be to take a packet capture in front of Apigee Ingress or on Apigee Ingress itself. This will help determine if the client is sending the SNI header for the TLS handshake.
- To run on Apigee Ingressin Google Kubernetes Engine, you would require SSH to the node running the ingress gateway and install toolbox and tcpdump.
tcpdump -n -i any -s 0 'host IP_Address' -w FILE_NAME
Where FILE_NAME is the name of the file, including path, where you want the packet capture output saved.
- Analyse the packet capture using Wireshark or a similar tool.
- Here's a sample analysis of a packet capture using Wireshark taken on Apigee Ingress.
.
- In the packet capture output, message #83 indicates that the Client (source) sent a "Client Hello" message to Apigee Ingress (destination).

- When you select the Client Hello message and examine the Handshake Protocol: Client Hello, you will see that the Extension: server_name is missing.
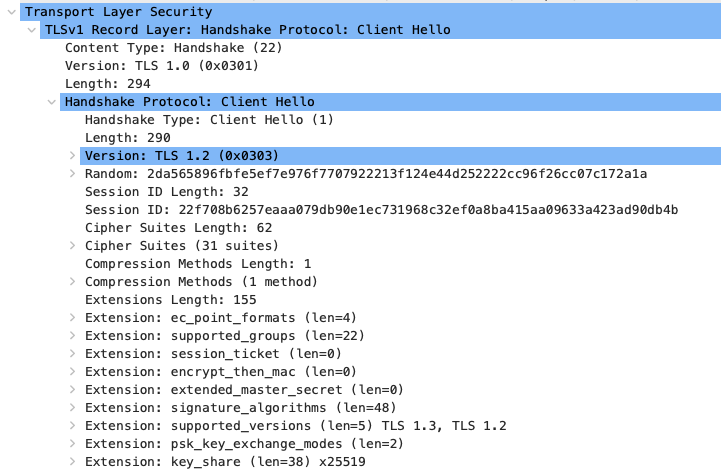
- As an example, an SNI enabled client will show Extension: server_name in the output as shown in the following example.
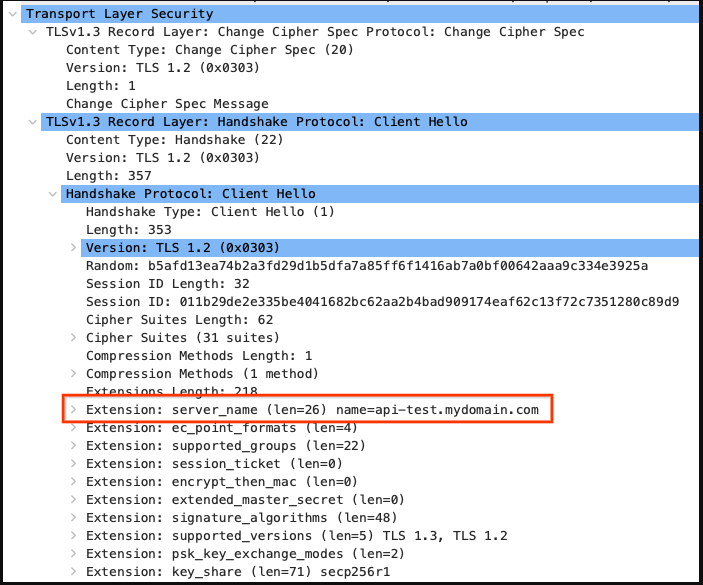
- This confirms that the client did not send the server_name to Apigee Ingress.
- Since no SNI server_name is included in the Client Hello message, no server certificate is returned, and Apigee Ingress closes the connection with an RST packet.
- In the packet capture output, message #83 indicates that the Client (source) sent a "Client Hello" message to Apigee Ingress (destination).
- Check if non-SNI clients are supported by testing an Apigee endpoint with a tool like OpenSSL to send requests with or without the SNI header.al.
- Check if non-SNI clients are enabled.
openssl s_client -connect api-test.mydomain.com:443 -noservername
Example Output
Connecting to 1.2.3.4 CONNECTED(00000005) write:errno=54 --- no peer certificate available --- No client certificate CA names sent --- SSL handshake has read 0 bytes and written 299 bytes Verification: OK --- New, (NONE), Cipher is (NONE) This TLS version forbids renegotiation. Compression: NONE Expansion: NONE No ALPN negotiated Early data was not sent Verify return code: 0 (ok) ---
- The response above shows no peer certificate available which means SNI clients are not enabled within the Apigee route, as we passed the -noservername option in the command. If a peer certificate was returned while using the -noservername flag, this would indicate a wildcard route is configured.
- Check if non-SNI clients are enabled.
- Review the current Apigee route configuration to see if a wildcard route is configured and enabled on the virtual host.
- Get a list of the defined Apigee routes with the following command:
kubectl -n apigee get apigeeroutes
Sample output
NAME STATE AGE myorg-hyb-dev-grp-000-33620d0 running 2d1h non-sni running 17s
- Check each Apigee route for hostnames that include a wildcard.
For each Apigee route, execute the provided command to retrieve a JSON array of its defined hostnames. A wildcard route will be indicated by an asterisk (
*) within the output.kubectl -n apigee get apigeeroute APIGEE_ROUTE_NAME
Example for
myorg-hyb-dev-grp-000-33620d0route:kubectl -n apigee get apigeeroute myorg-hyb-dev-grp-000-33620d0 -o jsonpath='{.spec.hostnames}'
Sample output
["api-test.mydomain.com"]
Example for
non-sniroute:kubectl -n apigee get apigeeroute non-sni -o jsonpath='{.spec.hostnames}'
Sample output
["*"]
The
non-sniapigeeroute is a wildcard route as it contains (*) as a hostname. - If a wildcard route is configured, then non-SNI clients are enabled.
- For the wildcard route, make sure the
enableNonSniClientflag is set to true. The following command runs on the wildcard route withnon-sniclient.kubectl -n apigee get apigeeroute non-sni -o jsonpath='{.spec.enableNonSniClient}'
Sample output
true - If the wildcard route exists and non-SNI clients are enabled, review the virtual host configuration in the
overrides.yamlfile to make sure that the wildcard route is listed in theadditionalGateways.virtualhosts: - name: dev-grp selector: app: apigee-ingressgateway ingress_name: ext-ingress sslCertPath: ./certs/keystore_dev-grp.pem sslKeyPath: ./certs/keystore_dev-grp.key additionalGateways: ["non-sni"]
- The
additionalGatewayswill show up in the Apigee route defined by your virtual host configuration. Use the following command to confirm your configuredadditionalGatewayis showing up in the Apigee route configuration.kubectl -n apigee get apigeeroute APIGEE_ROUTE_NAME -o jsonpath='{.spec.additionalGateways}
For example, the
myorg-hyb-dev-grp-000-33620d0route should show thenon-sniroute as anadditionalGateway.kubectl -n apigee get apigeeroute myorg-hyb-dev-grp-000-33620d0 -o jsonpath='{.spec.additionalGateways}'Sample output
["non-sni"]
Resolution
If the diagnostic steps indicate that your client is a non-SNI enabled client and non-SNI clients are not enabled or properly configured in your Apigee Hybrid installation, follow the enable non-SNI clients documentation to allow traffic from non-SNI clients.
Must gather diagnostic information
If the problem persists even after following the preceding instructions, gather the following diagnostic information and then contact Google Cloud Customer Care:Overrides.yaml- Output of the following commands
kubectl -n apigee get apigeeroutes- For each of the stated routes, run:
kubectl -n apigee describe apigeeroute - Environment Group(s) exhibiting the issue
- Get a list of the defined Apigee routes with the following command:
